 PDF(7824 KB)
PDF(7824 KB)


Screening of CMAS corrosion-resistant RE2SiO5 for environmental barrier coating application by a high-throughput multilayer stacking method
Liya Zheng, Keyu Ming, Zhilin Tian
Extreme Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (4) : 27-32.
 PDF(7824 KB)
PDF(7824 KB)
 PDF(7824 KB)
PDF(7824 KB)
Screening of CMAS corrosion-resistant RE2SiO5 for environmental barrier coating application by a high-throughput multilayer stacking method
High-temperature corrosion caused by low-melting-point molten salts known as CMAS poses a critical challenge to hot-section components in gas turbine engines. The screening of CMAS corrosion-resistant RE2SiO5 ceramics is crucial for the development of environmental barrier coatings for SiC fiber reinforced SiC composites. Due to varying experimental methods, conditions, and CMAS corrosion evaluation approaches, there has been some controversy regarding the CMAS resistance of RE2SiO5 ceramics. To address this issue, we employed a highthroughput multilayer stacking method to eliminate external influences such as experimental conditions. The CMAS resistance of several rare earth silicate ceramics was investigated, which revealed the influence of rare earth elements on CMAS corrosion. It was found that the smaller the rare earth ionic radius, the less corrosion product formed. Additionally, Er2SiO5 exhibited the best CMAS resistance due to the shallowest penetration depth of CMAS. The results indicate that the evaluation of CMAS corrosion resistance of RE2SiO5 ceramics requires a comprehensive consideration of the formation ability of corrosion products, dissolution of RE2SiO5, and the penetration of CMAS.
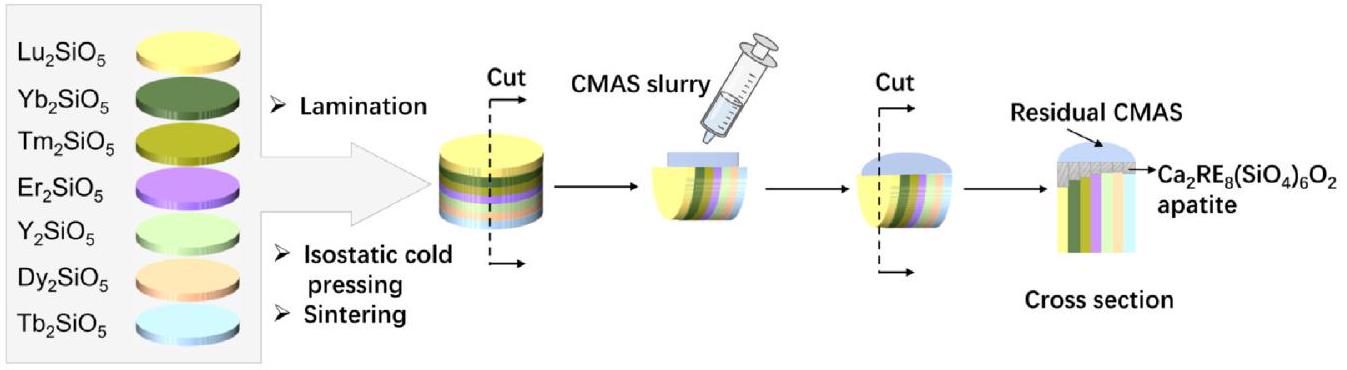
High-throughput screening / Environmental barrier coating / Rare earth silicate / CMAS corrosion / Multilayer stacking
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52202078 and 52202126).
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |