| $\mathrm{\Delta }{S}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}$ | Mixing Entropy | $\mathrm{\Delta }{S}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}=-R{\mathrm{\Sigma }}_{i}{c}_{i}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}{c}_{i}$ | Enthalpy change of a system when different components are mixed to form a homogeneous system. | [71] |
| $\mathrm{\Delta }{H}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}$ | Mixing Enthalpy | $\mathrm{\Delta }{H}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}={E}_{\text{HEC}\text{ }}-{\sum }_{i} {c}_{i}{E}_{i}$ | The sum of the interaction energy differences in the ideal state. | [72] |
| $\mathrm{\Omega }$ | Entropy-Enthalpy Balance Factor | $\mathrm{\Omega }=\frac{{T}_{\mathrm{m}}\mathrm{\Delta }{S}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}}{\left|\mathrm{\Delta }{H}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}\right|}$ | Tm is the isothermal temperature. | [73] |
| $\delta $ | Atomic (ion) Radius Difference | $\delta ={\left[{\sum }_{i} {c}_{i}\left(1-\frac{{r}_{i}}{\stackrel{‾}{r}}\right)\right]}^{1/2},\stackrel{‾}{r}={\sum }_{i} {c}_{i}{r}_{i}$ | Contribution of differences in atomic/ionic radii of components to lattice distortion | [74] |
| $\mathrm{\Delta }\chi $ | Electronegativity Difference | $\mathrm{\Delta }\chi =\sqrt{{\sum }_{i} {c}_{i}{\left({\chi }_{i}-\stackrel{‾}{\chi }\right)}^{2}},\stackrel{‾}{\chi }={\sum }_{i} {c}_{i}{\chi }_{i}$ | $\mathrm{\Delta }\chi $ reflects the difference in electronegativity between different elements. | [75] |
| VEC | Valence Electron Concentration | $VEC={\sum }_{i} {c}_{i}VE{C}_{i}$ | Reflects the degree of electron filling and energy band structure characteristics of the system | [74] |
| DEED | Disordered Enthalpy-Entropy Descriptor | $DEED=\sqrt{\frac{{\sigma }_{\mathrm{\Omega }}^{-1}\left[{H}_{\mathrm{f}}\right]}{{⟨\mathrm{\Delta }{H}_{\mathrm{h}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{l}}⟩}_{\mathrm{\Omega }}}}$ | Predicting the possibility of single-phase disordered structures in multicomponent systems, Hf and Hhull are the DFT formation energies of the partial occupation POCC tiles and the convex hull, respectively. | [76] |
| EFA | Entropy Forming Ability | $EFA={\left[\frac{\left({\sum }_{i=1}^{n} {g}_{i}\right)-1}{{\sum }_{i=1}^{n} {g}_{i}{\left({H}_{i}-{H}_{\text{mix}\text{ }}\right)}^{2}}\right]}^{1/2}$ | Entropy-driven formation of stable single-phase solid solutions, where n is the total number of sampled geometrical configurations and gi are their degeneracies. Hi of the sampled configurations. | [66] |
| LDI | Lattice Distortion Index | $LDI={\sum }_{i=1}^{n} \sqrt{{\left({x}_{i,a}-{x}_{i,0}\right)}^{2}+{\left({y}_{i,a}-{y}_{i,0}\right)}^{2}+{\left({z}_{i,a}-{z}_{i,0}\right)}^{2}}/n$ | Parameters for the degree of lattice distortion in disordered systems, ( x,y,z ) is the atomic position. | [77] |
| $\gamma $ | The normalized geometric packing parameter for the metallic sublattice calculated | $\gamma =\left\{1-{\left[1-\frac{{\left({r}_{\mathrm{S}}+\stackrel{‾}{r}\right)}^{2}-{\stackrel{‾}{r}}^{2}}{{\left({r}_{\mathrm{S}}+\stackrel{‾}{r}\right)}^{2}}\right]}^{1/2}\right\}/\left\{1-{\left[1-\frac{{\left({r}_{\mathrm{L}}+\stackrel{‾}{r}\right)}^{2}-{\stackrel{‾}{r}}^{2}}{{\left({r}_{\mathrm{L}}+\stackrel{‾}{r}\right)}^{2}}\right]}^{1/2}\right\}$ | Evaluating how different metal atoms stack together in a crystal lattice, where rS and rL are the radii of the smallest and largest atoms. | [78] |
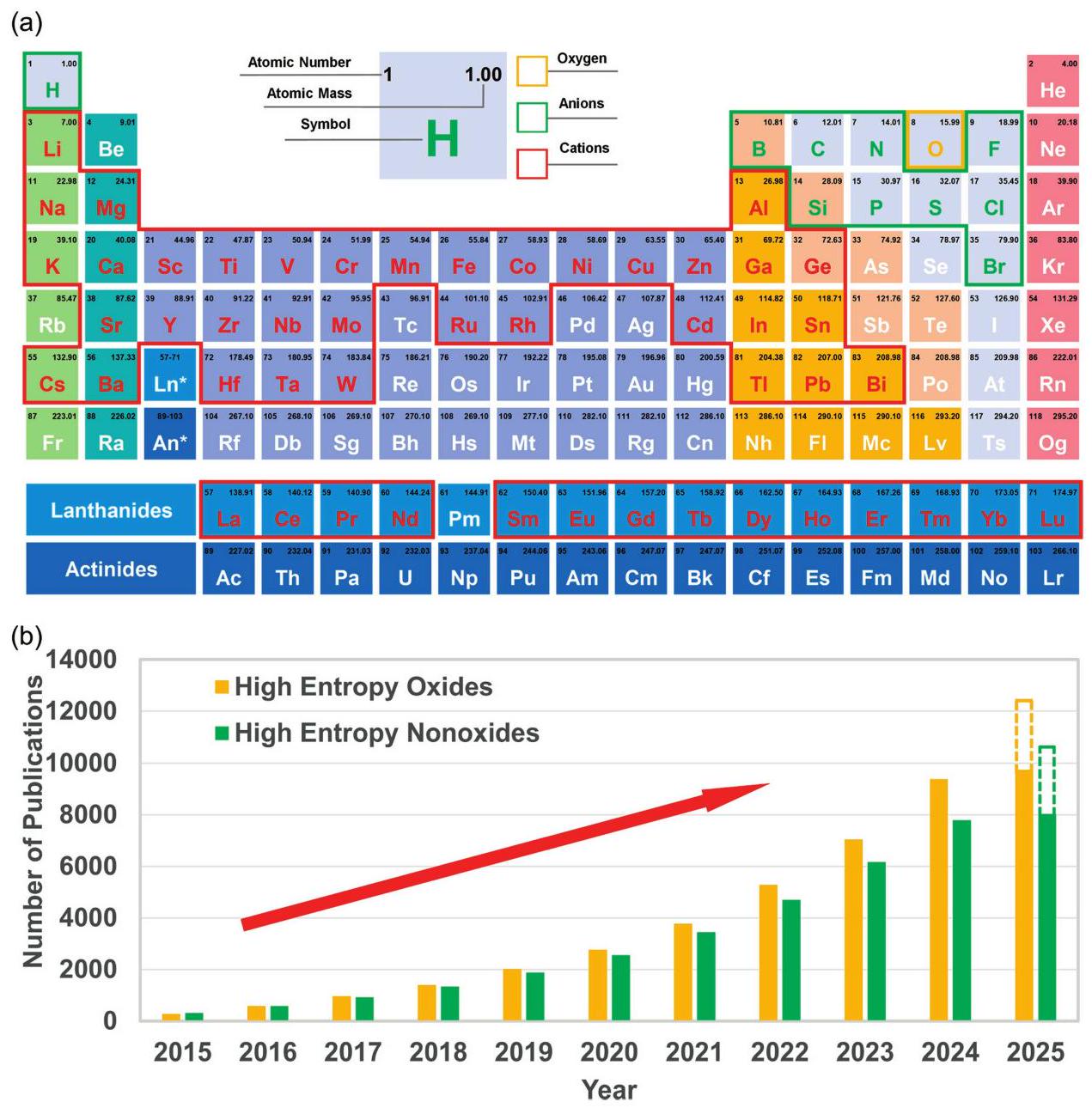 Fig. 1. (a) All the constituent elements reported in HECs to date. (b) Total number of publications on major HECs over the last decade. Data was retrieved from Web of Science on February 28, 2025, using keywords: "high-entropy", "oxide", "boride", "carbide", "nitride", "silicide", "fluoride", "hydride", "phosphide", "sulfide", and "ceramics".
Fig. 1. (a) All the constituent elements reported in HECs to date. (b) Total number of publications on major HECs over the last decade. Data was retrieved from Web of Science on February 28, 2025, using keywords: "high-entropy", "oxide", "boride", "carbide", "nitride", "silicide", "fluoride", "hydride", "phosphide", "sulfide", and "ceramics".
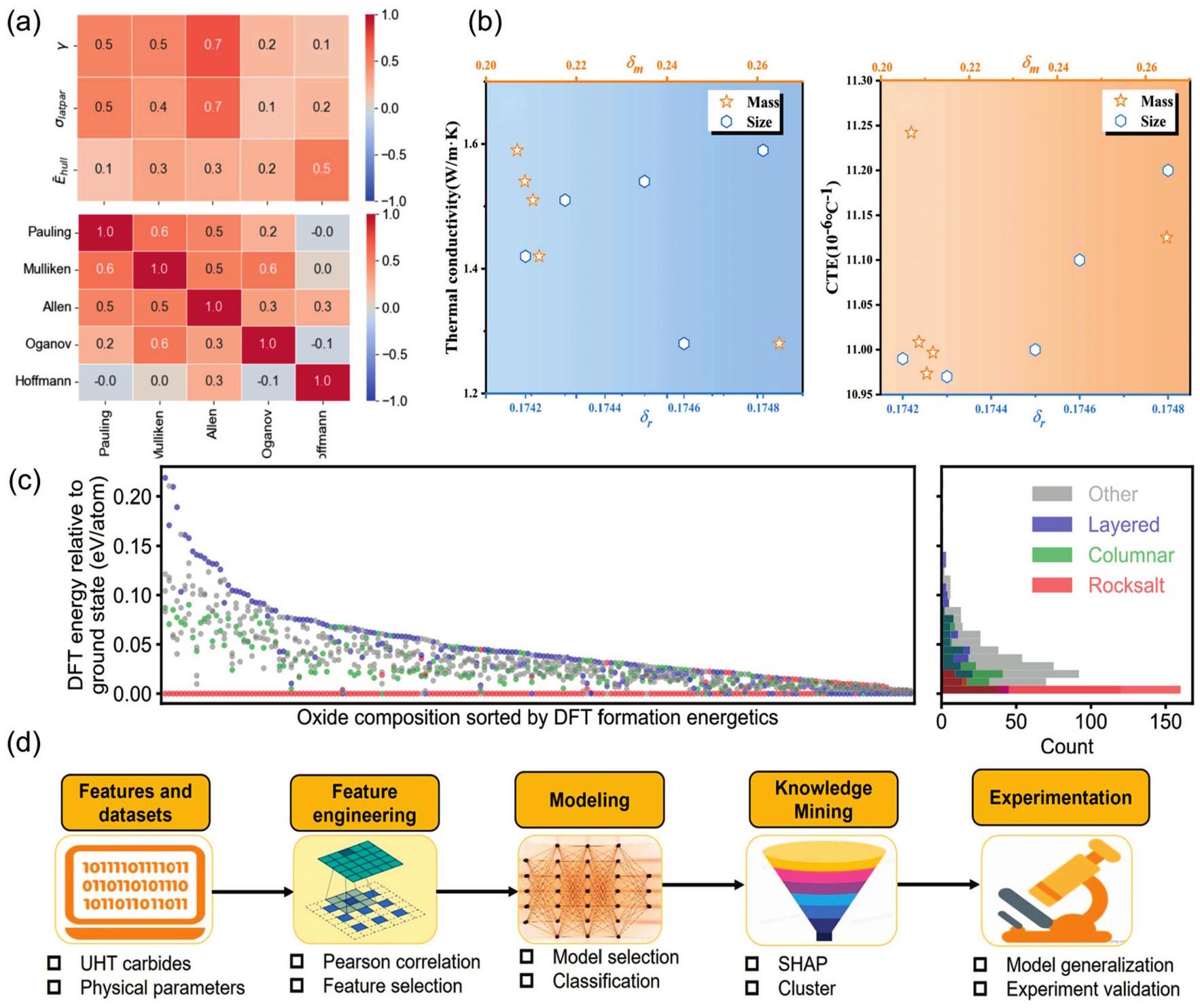 Fig. 2. (a) Pairwise correlations of computational parameters: atomic radius deviations, lattice parameters, stabilization factors for miscible binary carbides, and electrochemical factors on different scales (top); correlations between different electronegativity scales (bottom). Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 2. (a) Pairwise correlations of computational parameters: atomic radius deviations, lattice parameters, stabilization factors for miscible binary carbides, and electrochemical factors on different scales (top); correlations between different electronegativity scales (bottom). Reproduced from Ref [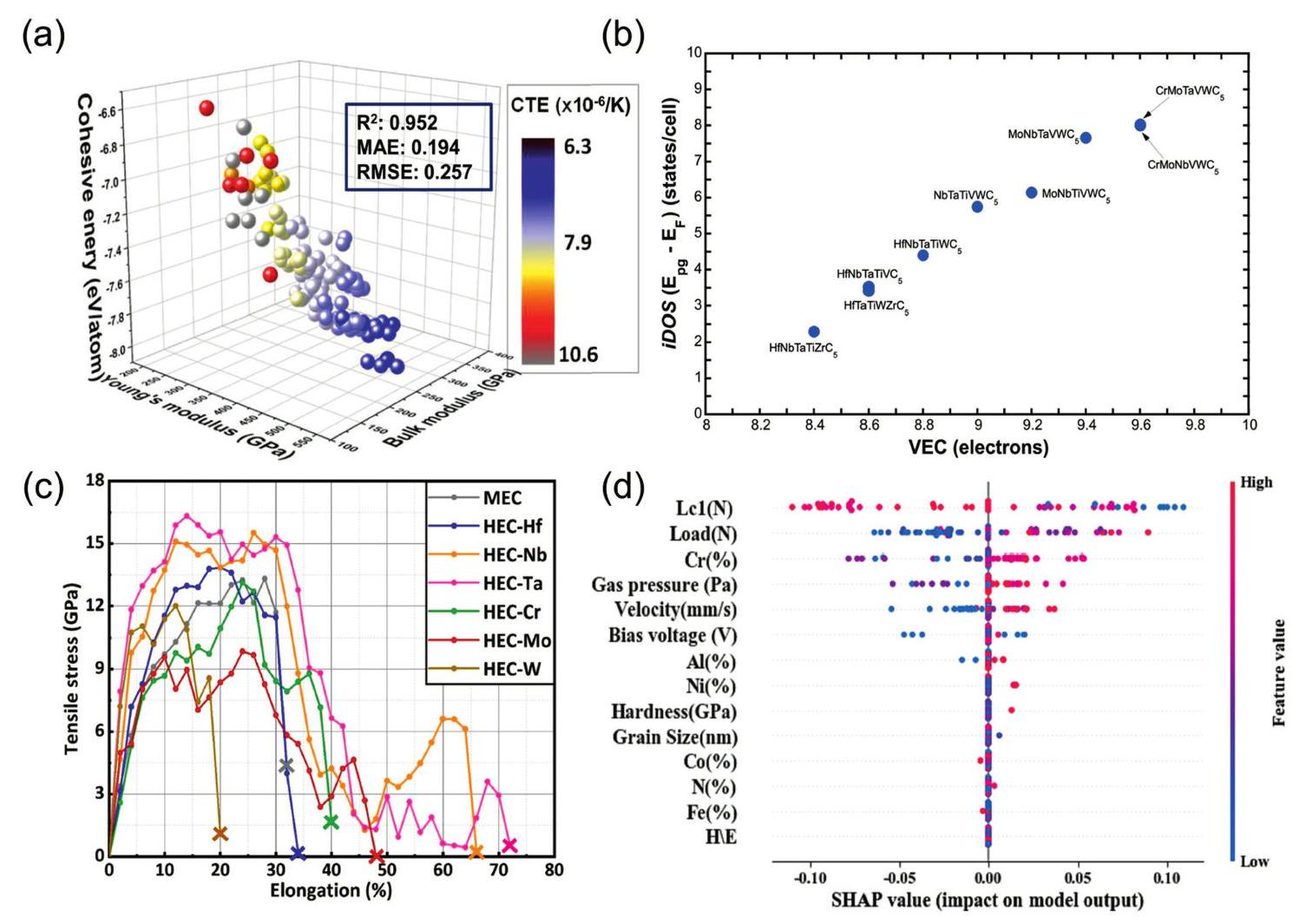 Fig. 3. (a) The 3D plots of the NET (neural network) training set were generated based on three parameters (bulk modulus, Young's modulus, and cohesive energy). Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 3. (a) The 3D plots of the NET (neural network) training set were generated based on three parameters (bulk modulus, Young's modulus, and cohesive energy). Reproduced from Ref [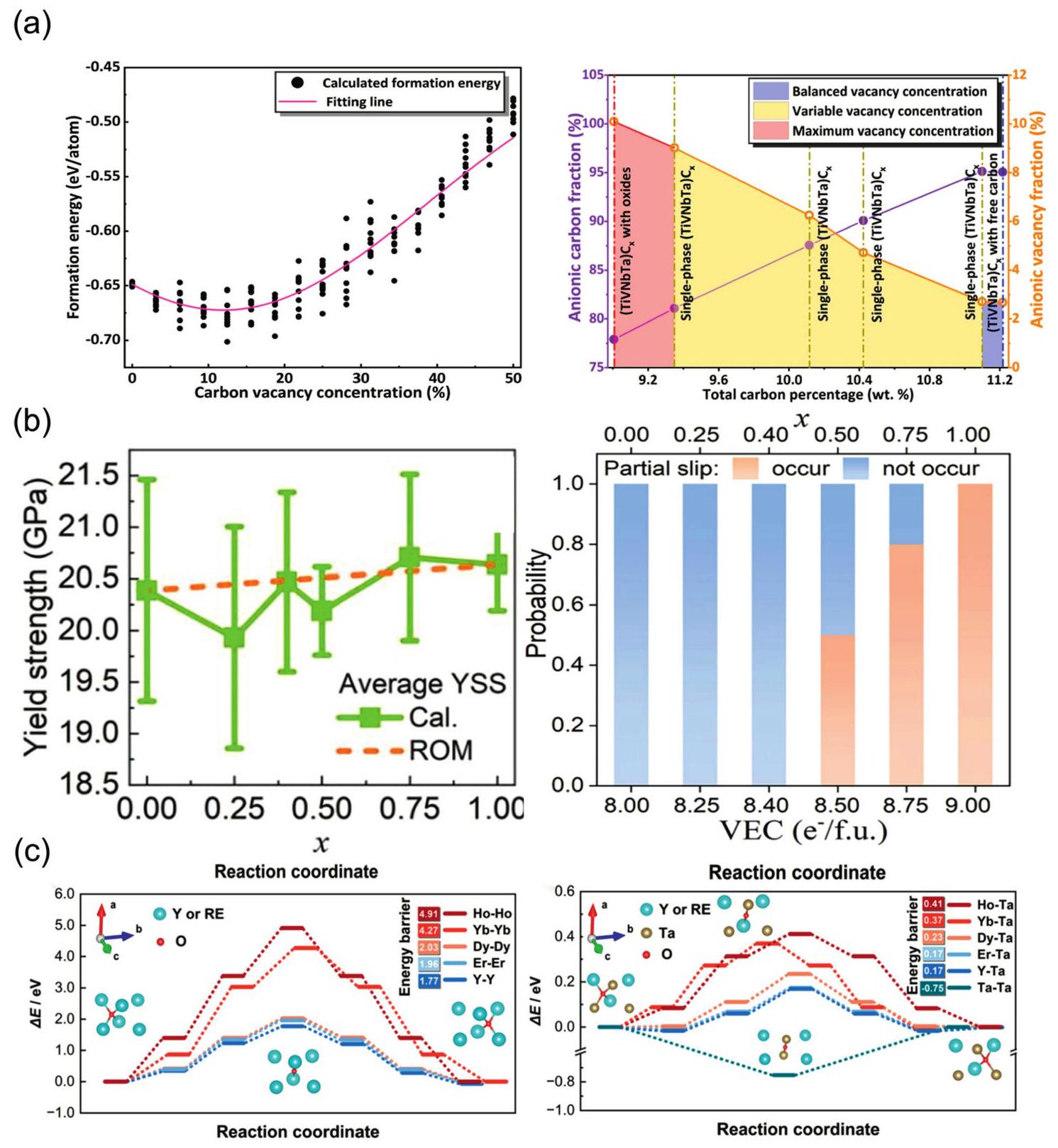 Fig. 4. (a) The fitting formation energy curve of (TiVNbTa)Cx with variation of anionic vacancy concentration; Curves of anionic carbon and vacancy fraction under changing carbon content. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 4. (a) The fitting formation energy curve of (TiVNbTa)Cx with variation of anionic vacancy concentration; Curves of anionic carbon and vacancy fraction under changing carbon content. Reproduced from Ref [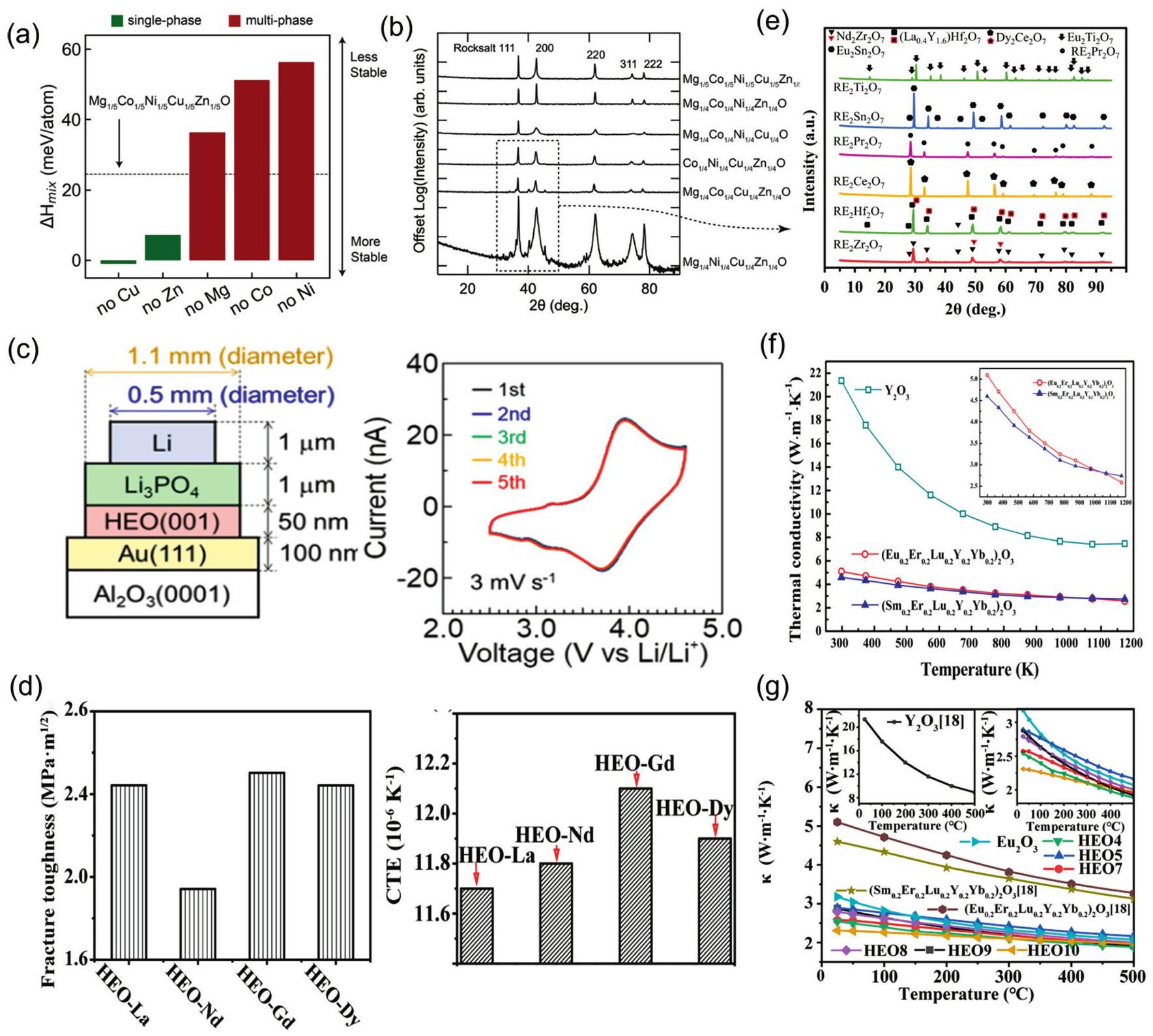 Fig. 6. (a) X-ray diffractograms of four-component derivatives of (MgCoNiCuZn)O as a substrate; (b) DFT analysis of four diffractive phase compositions by mixing enthalpy. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 6. (a) X-ray diffractograms of four-component derivatives of (MgCoNiCuZn)O as a substrate; (b) DFT analysis of four diffractive phase compositions by mixing enthalpy. Reproduced from Ref [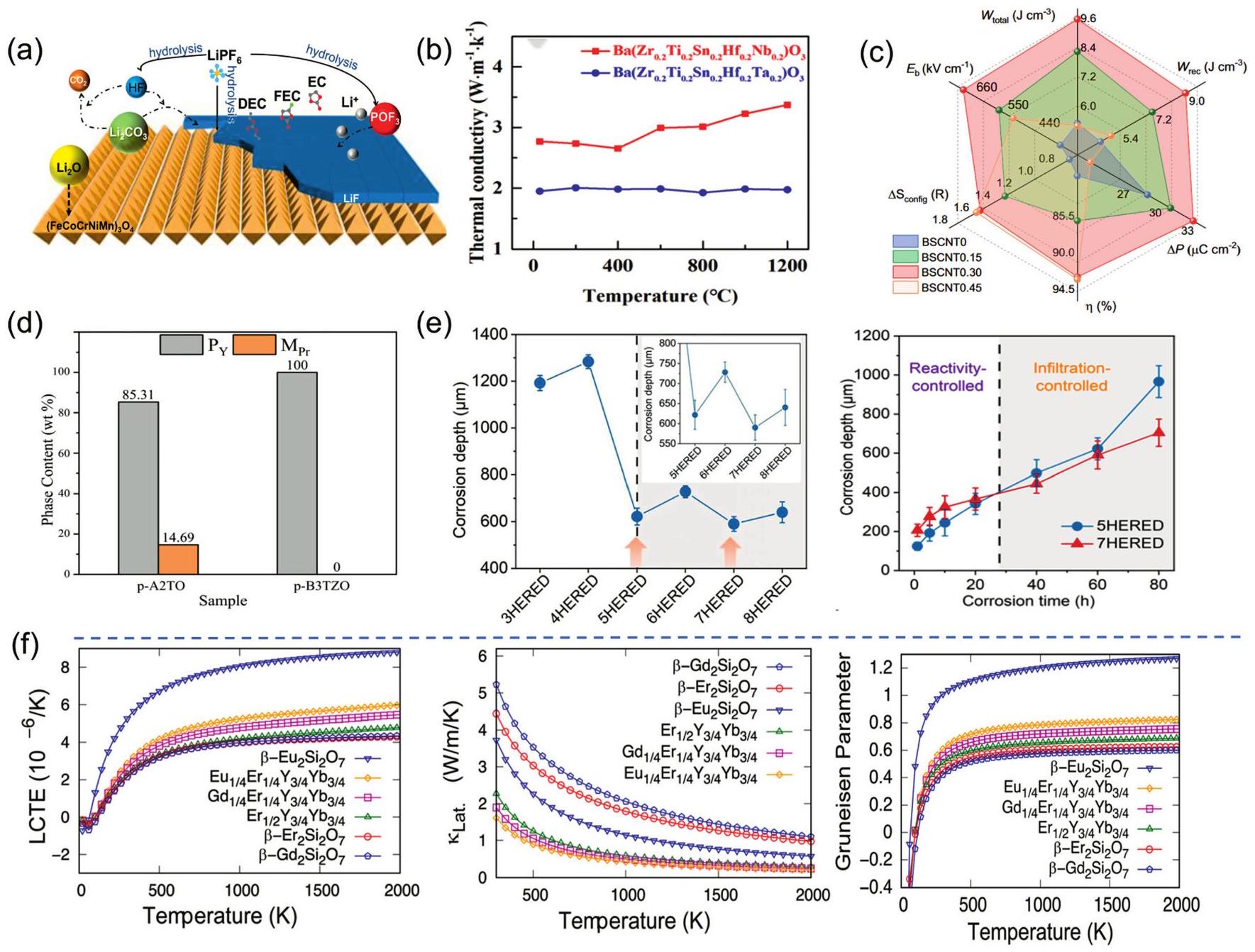 Fig. 7. (a) Schematic diagram representation of the conversion of Li2O,LiF, and Li2CO3 during the cycling process of the preconditioned HEOs. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 7. (a) Schematic diagram representation of the conversion of Li2O,LiF, and Li2CO3 during the cycling process of the preconditioned HEOs. Reproduced from Ref [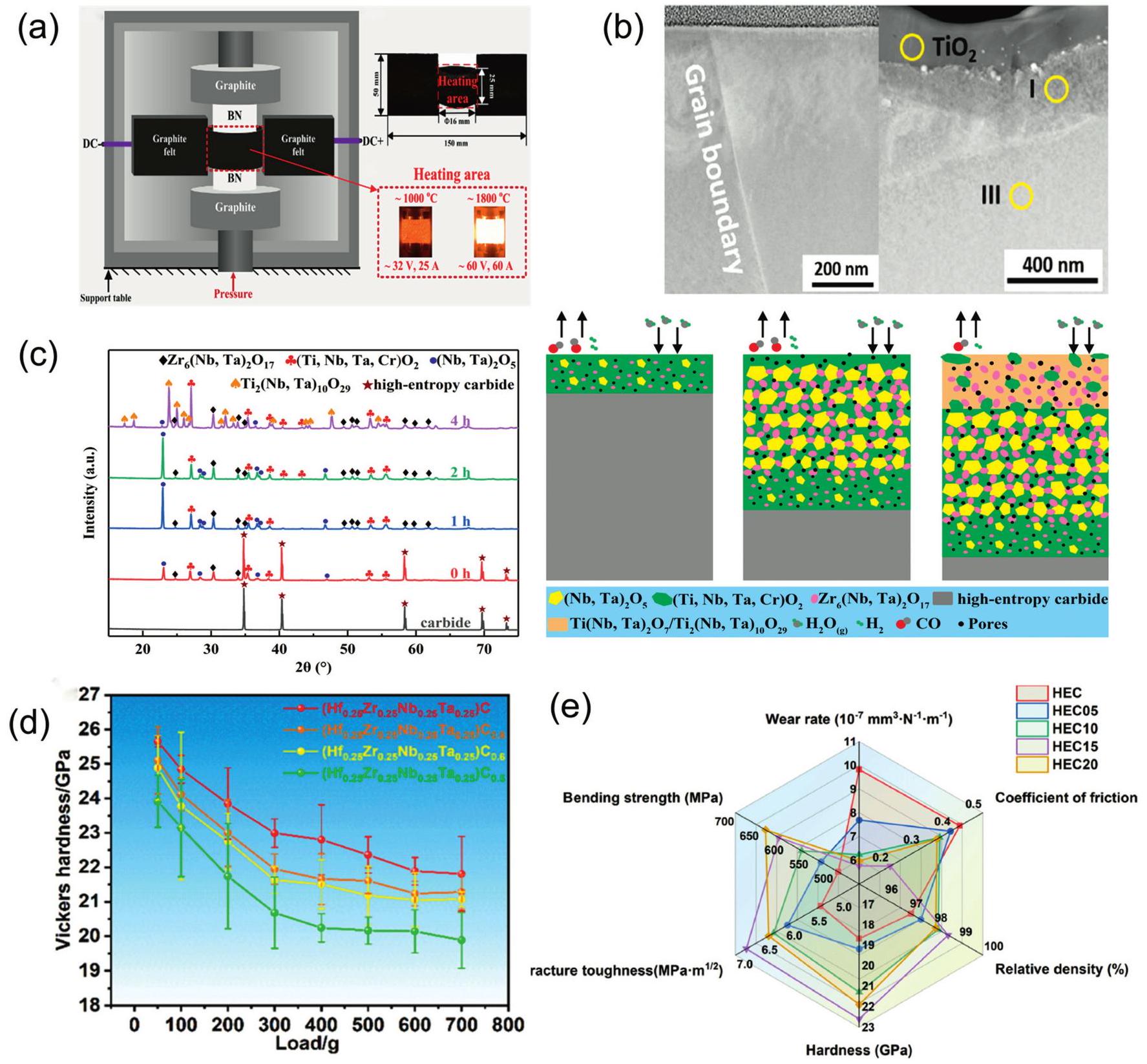 Fig. 8. (a) Schematic diagram of ultra-fast pressure sintering apparatus. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 8. (a) Schematic diagram of ultra-fast pressure sintering apparatus. Reproduced from Ref [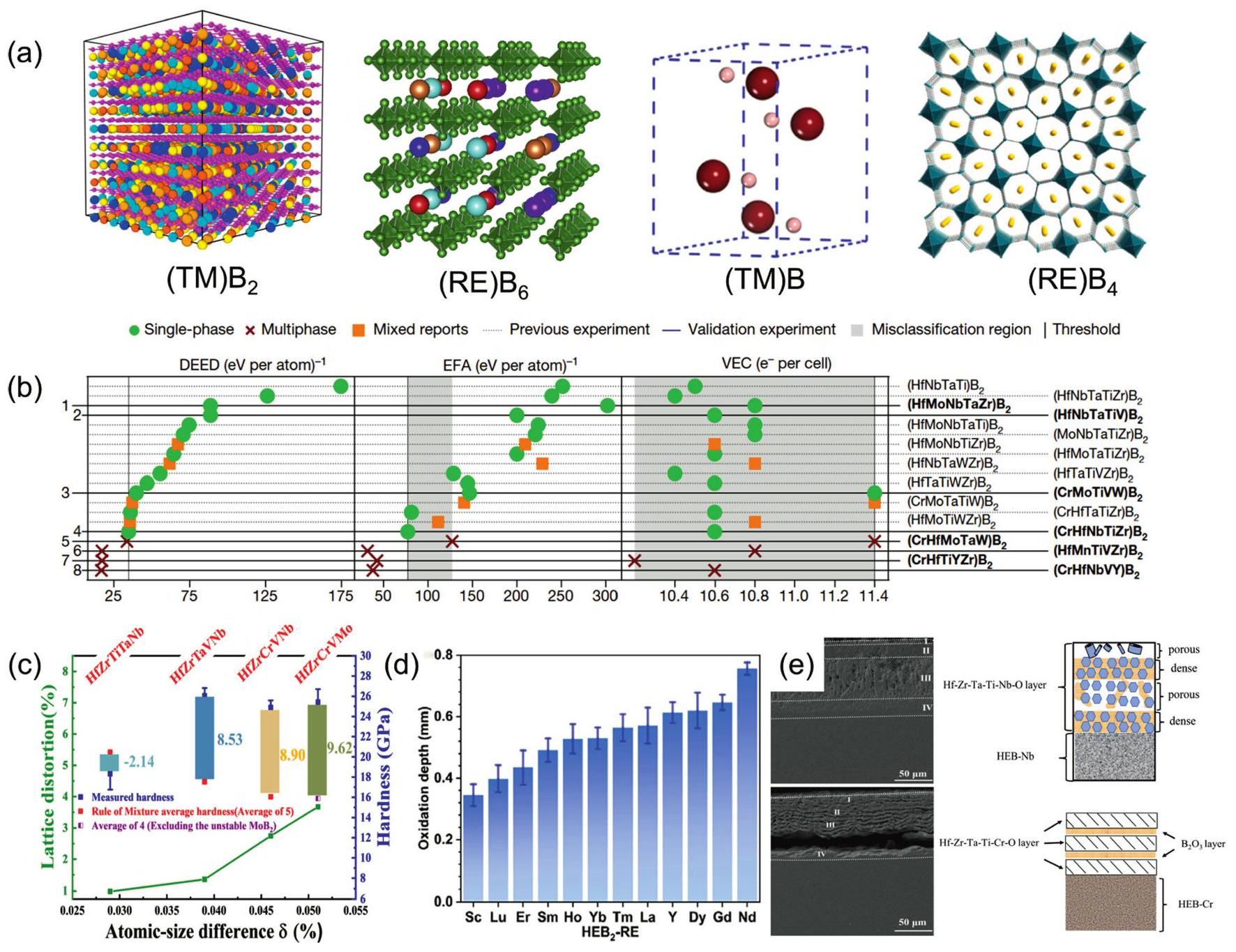 Fig. 9. (a) Crystal structures of different HEBs. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 9. (a) Crystal structures of different HEBs. Reproduced from Ref [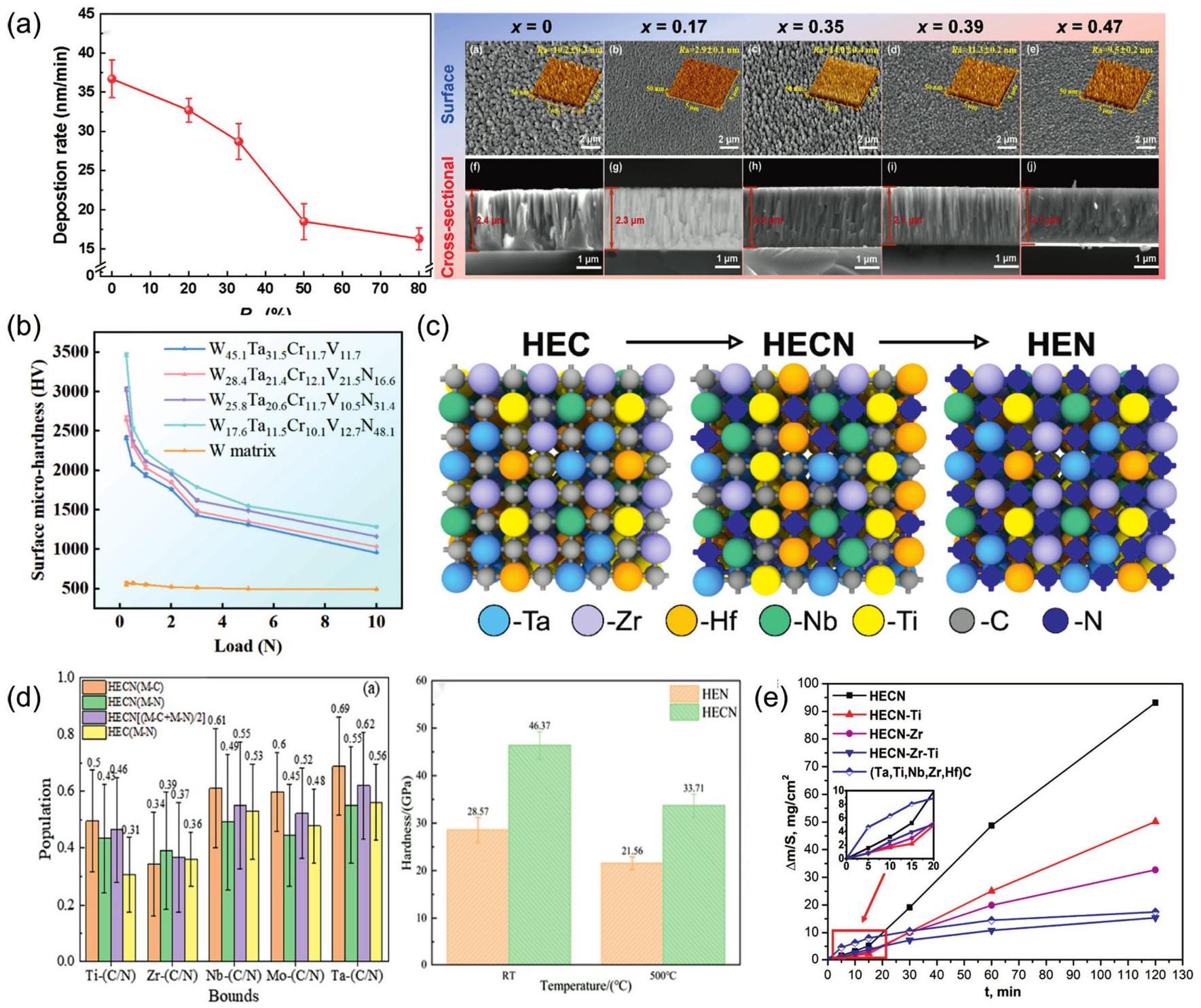 Fig. 10. (a) SEM images of surface and cross-sectional morphology of (MoNbTaTiZr) 1-x Nx coatings under different x; Deposition rates of (MoNbTaTiZr) 1-x Nx coatings with different RN. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 10. (a) SEM images of surface and cross-sectional morphology of (MoNbTaTiZr) 1-x Nx coatings under different x; Deposition rates of (MoNbTaTiZr) 1-x Nx coatings with different RN. Reproduced from Ref [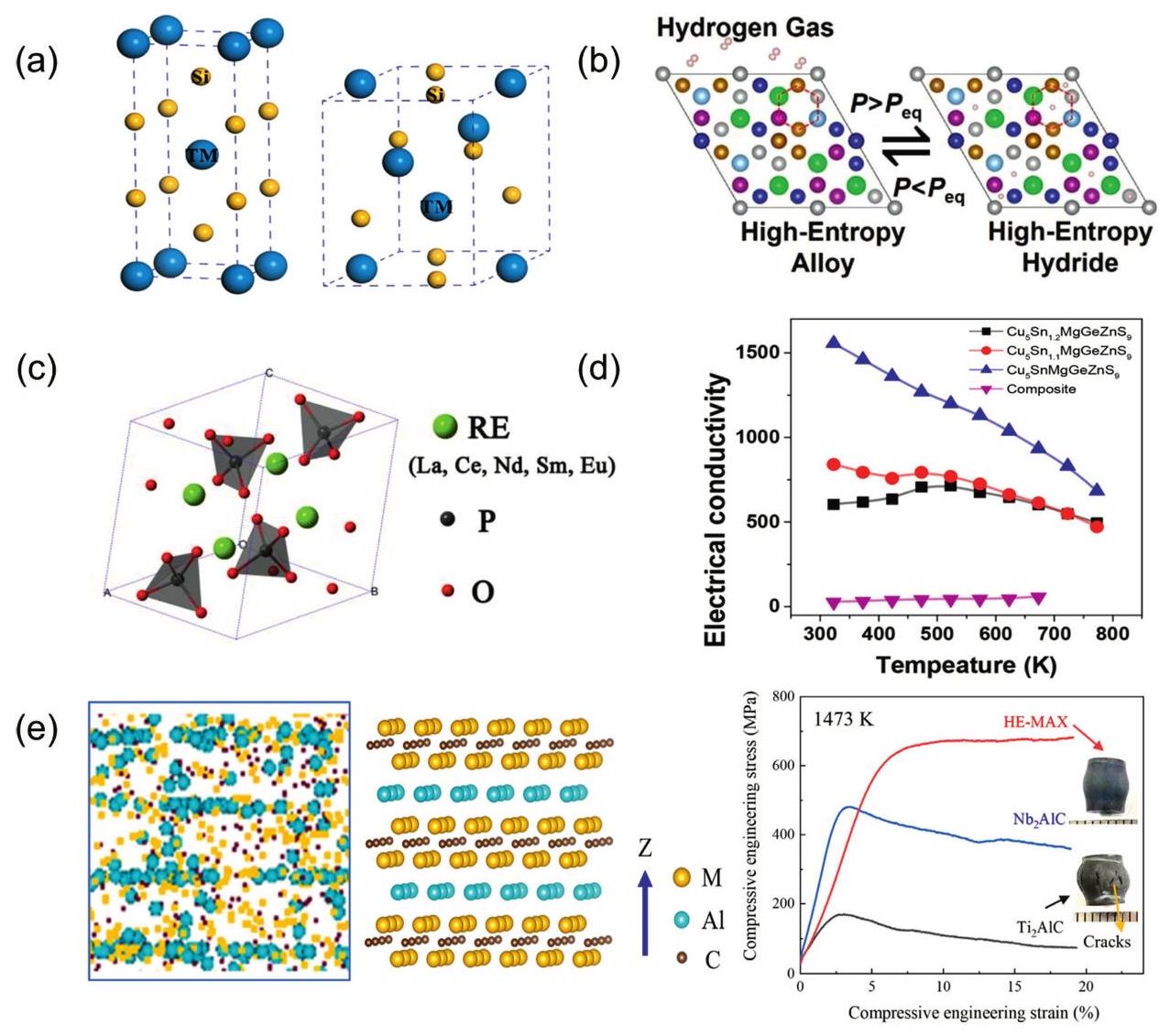 Fig. 11. (a) Crystal structure of tetragonal transition metal disilicide (left), hexagonal transition metal disilicides (right). Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 11. (a) Crystal structure of tetragonal transition metal disilicide (left), hexagonal transition metal disilicides (right). Reproduced from Ref [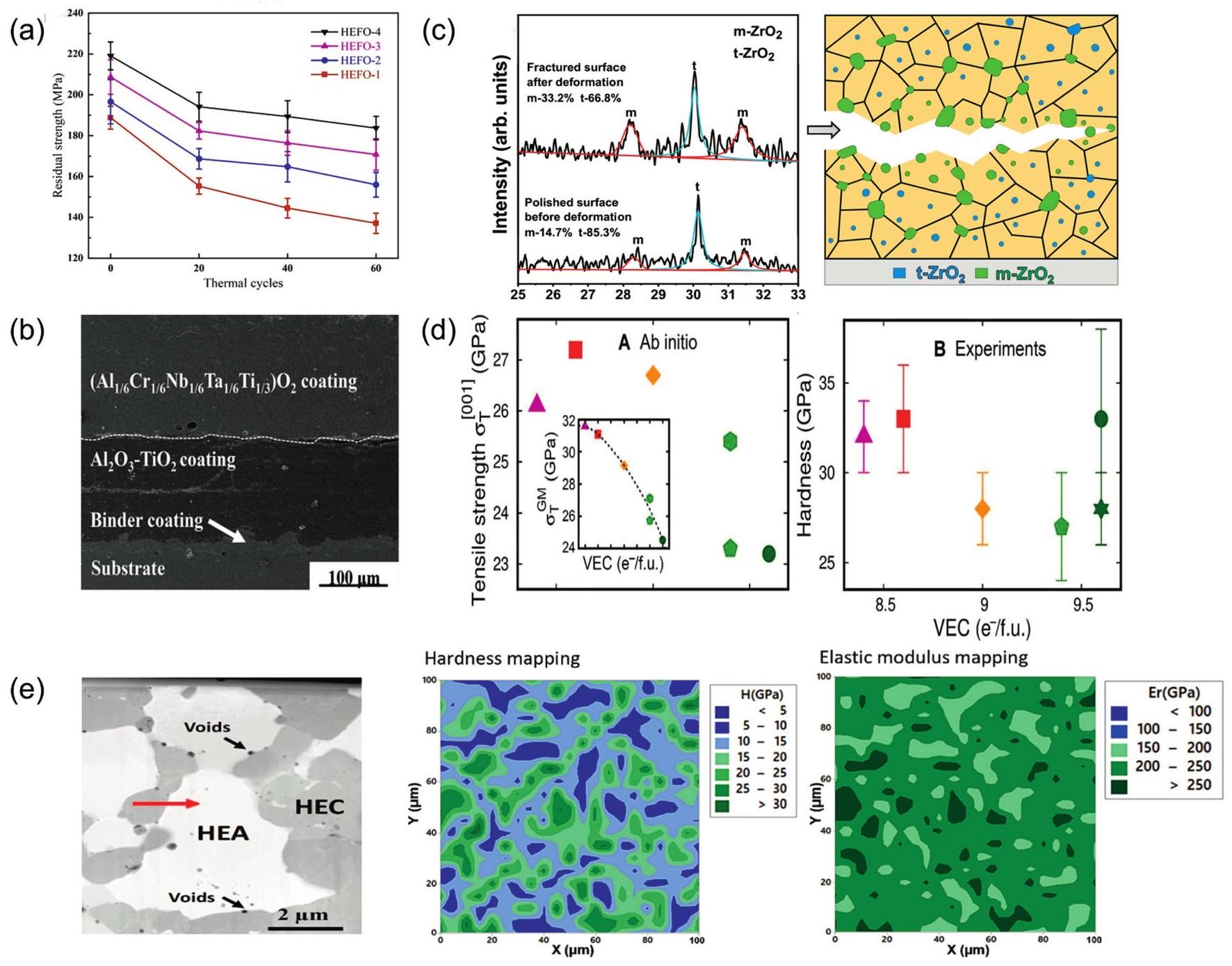 Fig. 12. (a) Residual flexural strength after cyclic thermal shock at
Fig. 12. (a) Residual flexural strength after cyclic thermal shock at 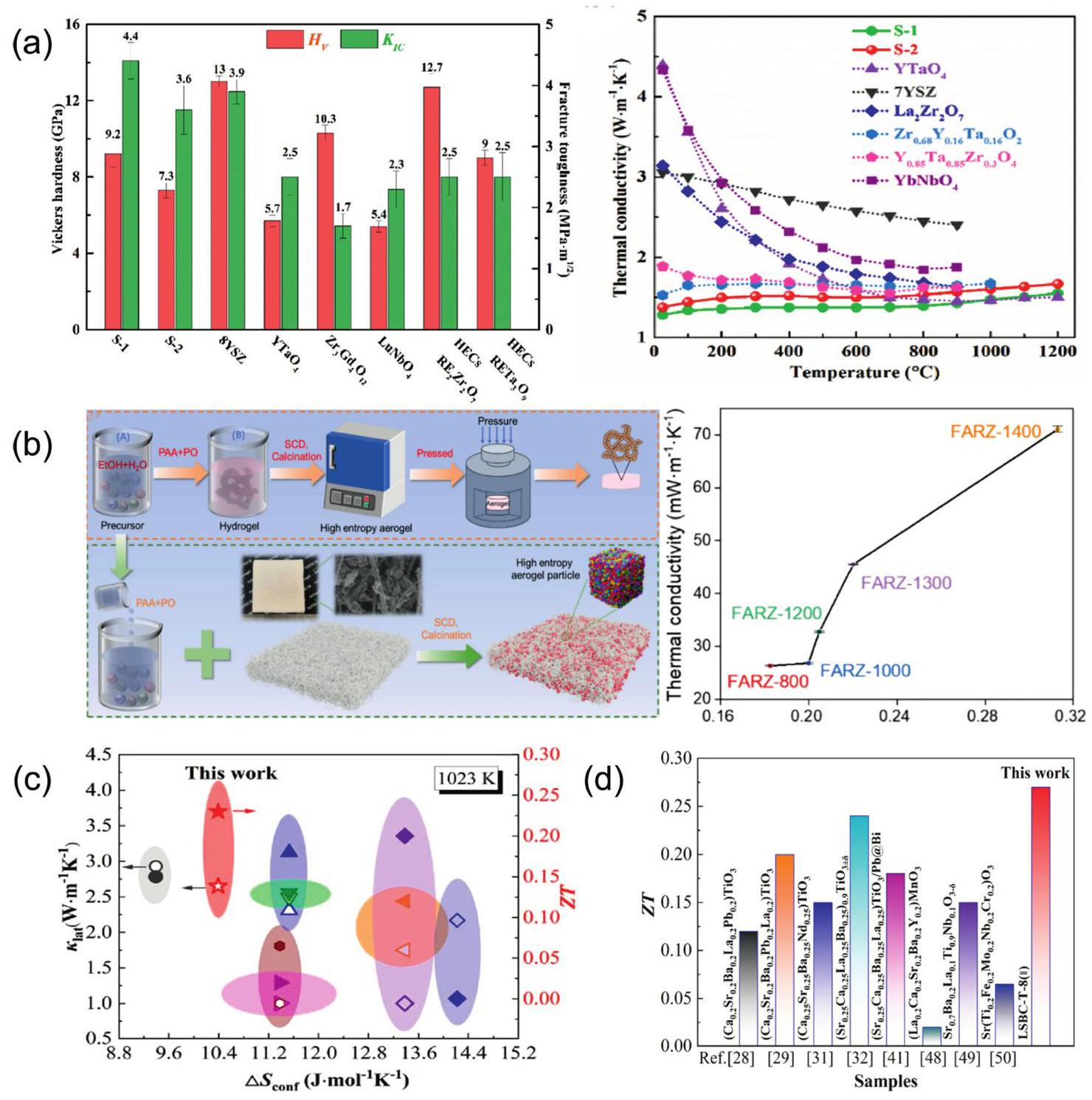 Fig. 13. (a) Mechanical property comparisons between dual-phase zirconate/tantalate HECs, 8YSZ, YTaO4, and others. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 13. (a) Mechanical property comparisons between dual-phase zirconate/tantalate HECs, 8YSZ, YTaO4, and others. Reproduced from Ref [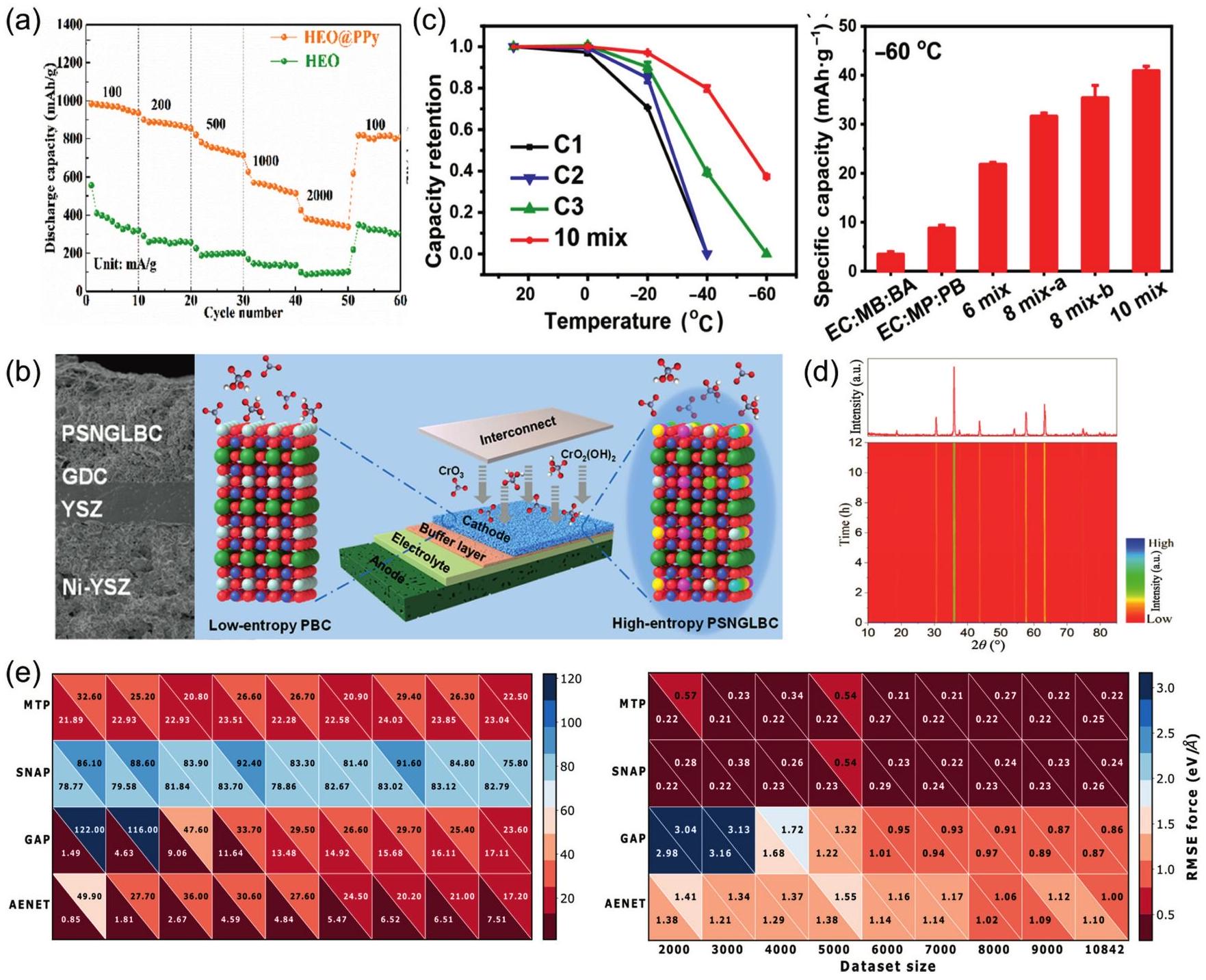 Fig. 14. (a) The rate discharge performance of HEO and HEO@PPy at various current densities; the rate performance of HEO@PPy significantly outperforms that of HEO. Reproduced from Ref [
Fig. 14. (a) The rate discharge performance of HEO and HEO@PPy at various current densities; the rate performance of HEO@PPy significantly outperforms that of HEO. Reproduced from Ref [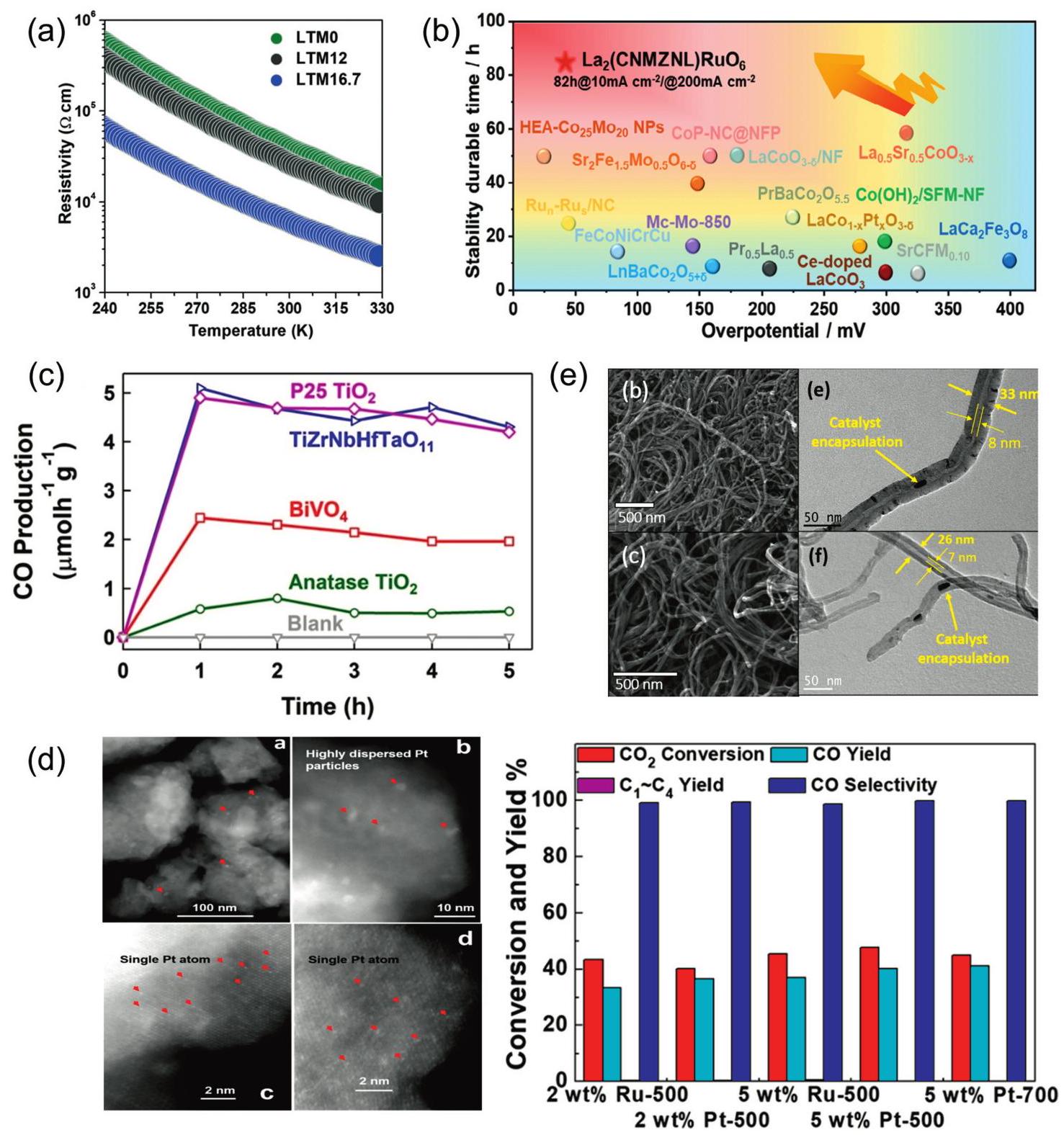 Fig. 15. (a) Temperature-dependent (
Fig. 15. (a) Temperature-dependent ( 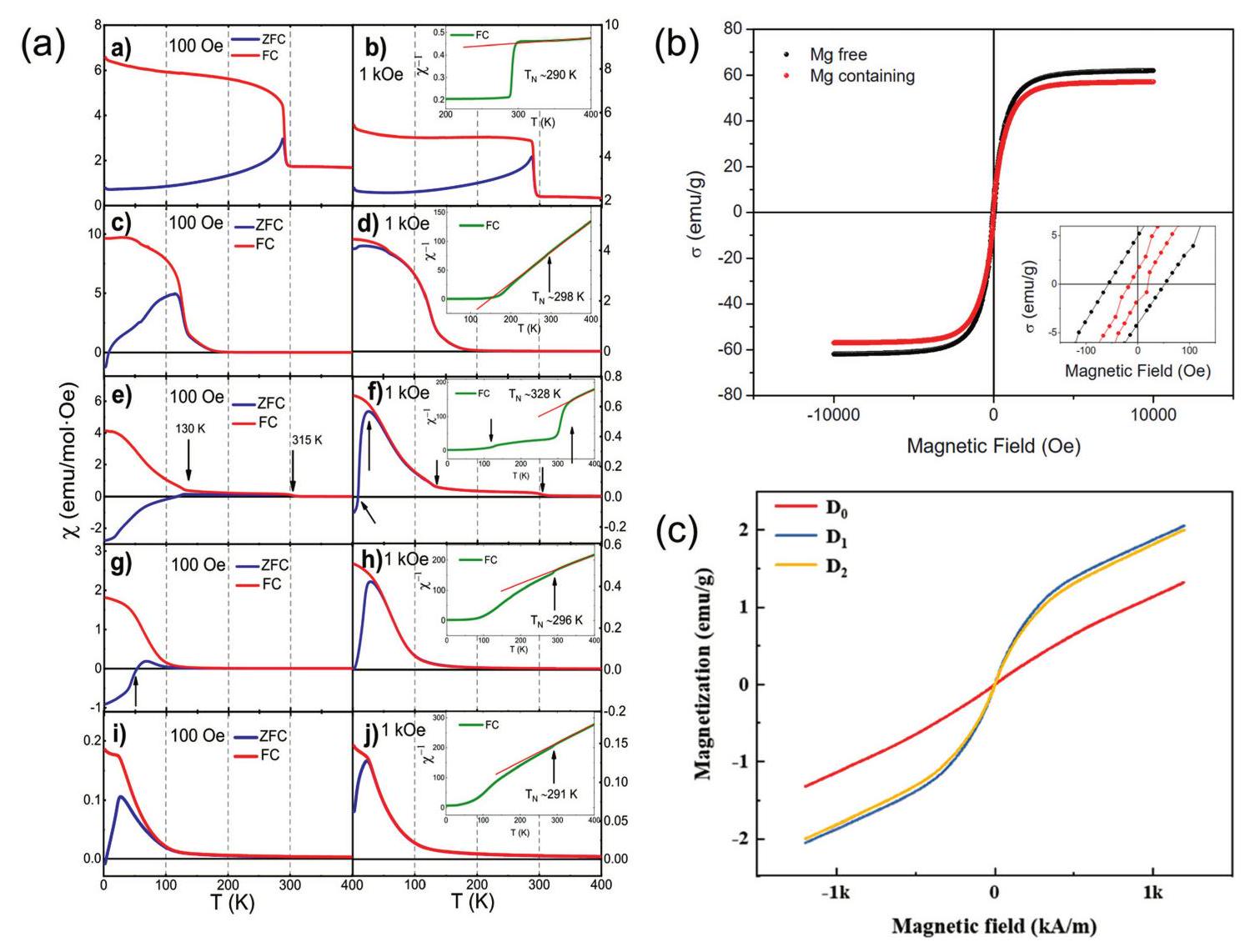 Fig. 16. (a) Magnetic induction strength versus temperature for (a-b) LC, (c-d) LCM, (e-f) LCMF, (g-h) LCMFA, and (i-j) LCMFAG ceramics in ZFC (Zero Field Cooling) and FC (Field Cooling) modes at 100 Oe and 1000 Oe, inset show the
Fig. 16. (a) Magnetic induction strength versus temperature for (a-b) LC, (c-d) LCM, (e-f) LCMF, (g-h) LCMFA, and (i-j) LCMFAG ceramics in ZFC (Zero Field Cooling) and FC (Field Cooling) modes at 100 Oe and 1000 Oe, inset show the 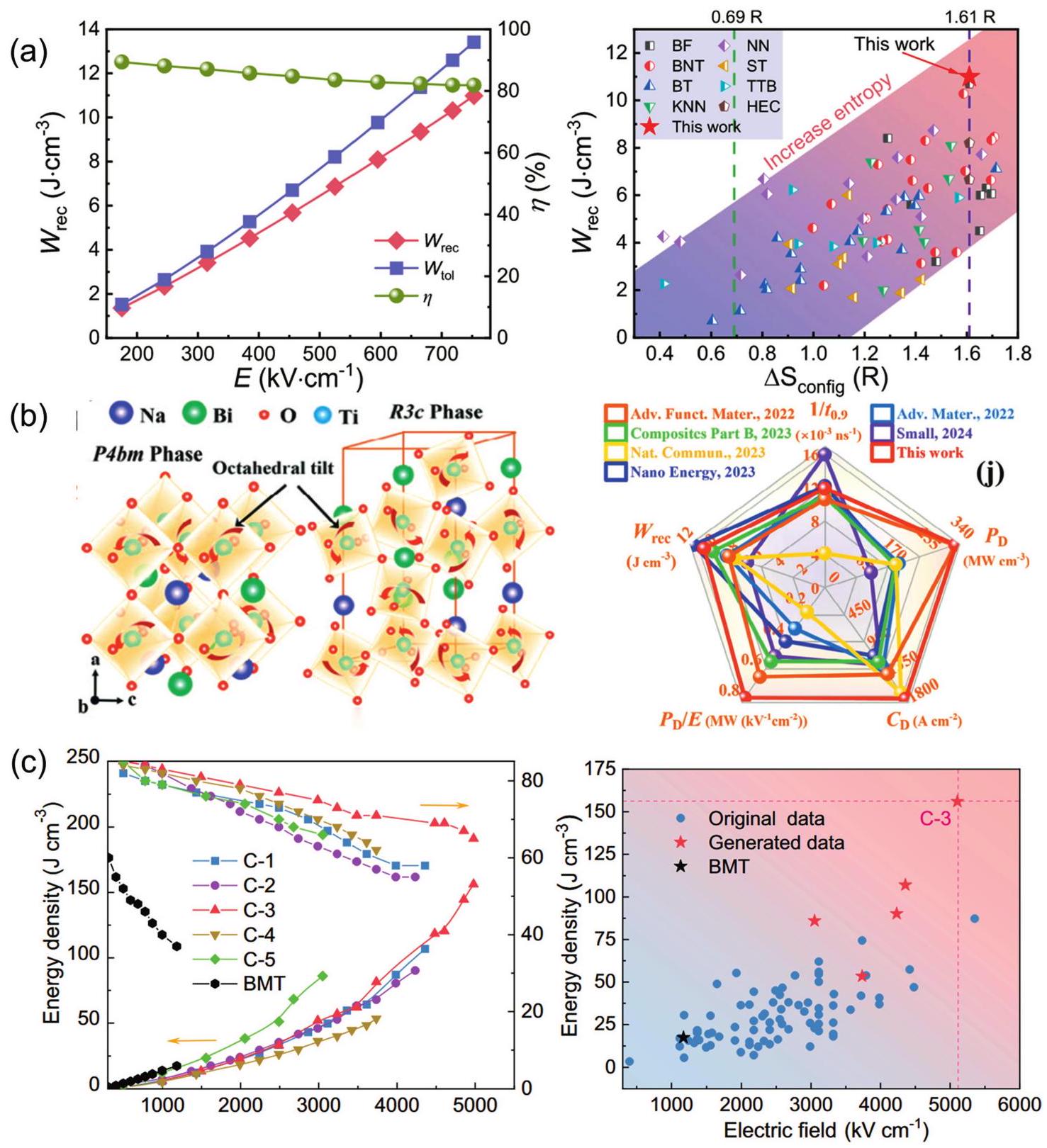 Fig. 17. (a) Wrec and
Fig. 17. (a) Wrec and 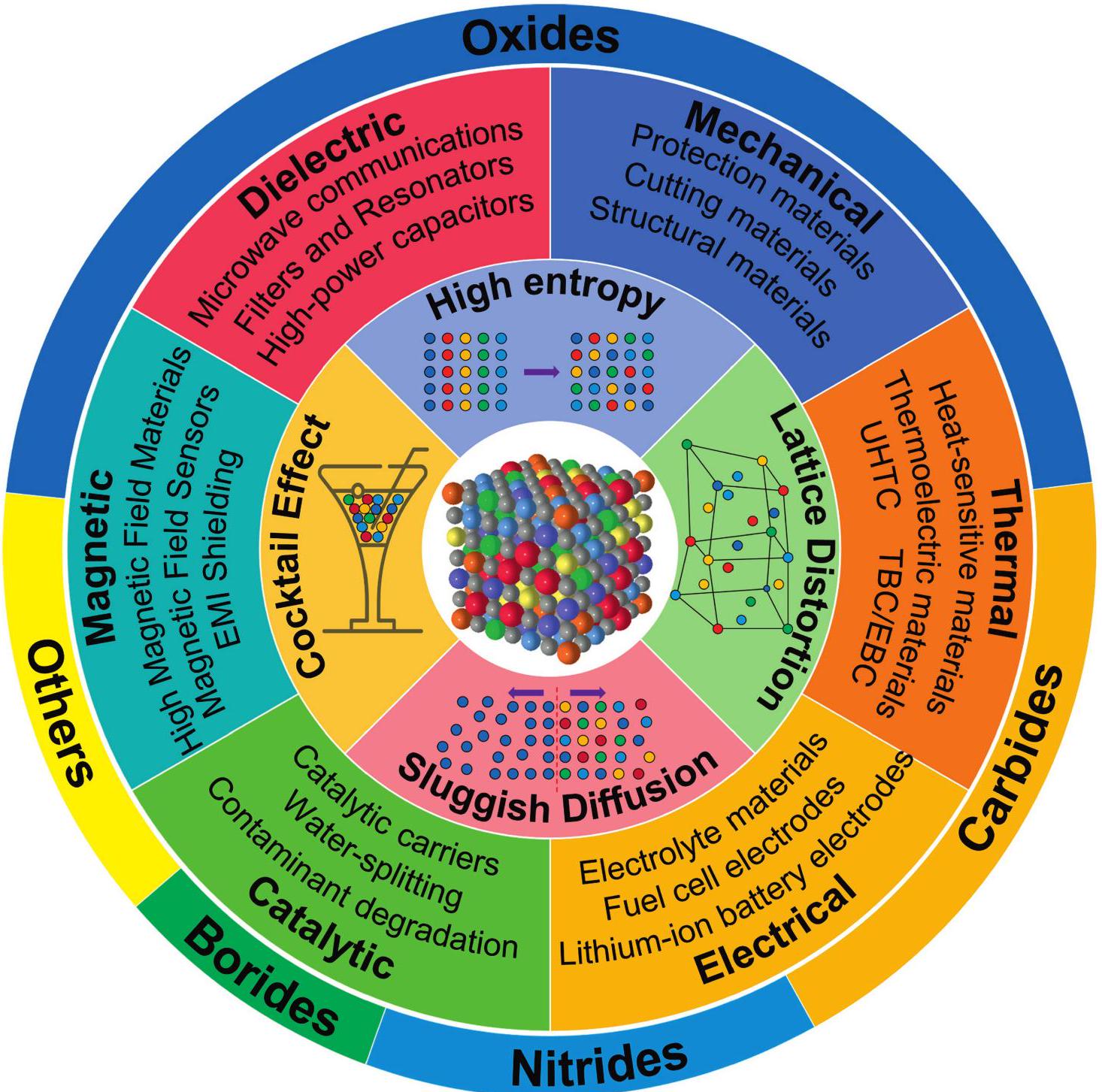 Fig. 18. An overview diagram of HECs. The outer ring shows the percentage of studies on high-entropy oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides and others. The inner rings show the main applications of HECs, as well as the four core effects of high-entropy materials and a schematic of the disordered structure, respectively.
Fig. 18. An overview diagram of HECs. The outer ring shows the percentage of studies on high-entropy oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides and others. The inner rings show the main applications of HECs, as well as the four core effects of high-entropy materials and a schematic of the disordered structure, respectively.