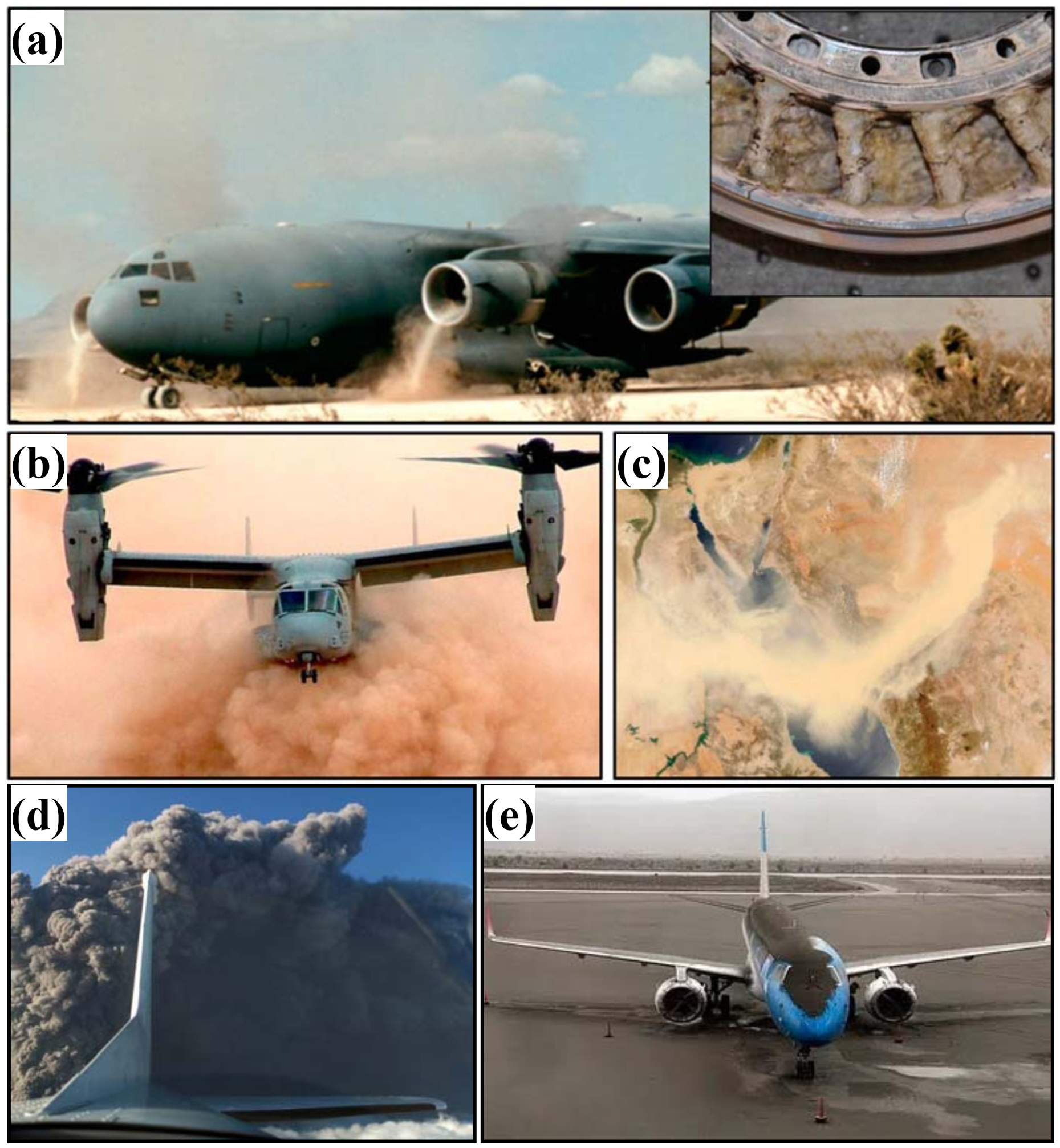
 Fig. 3 (a) C-17 military aircraft ingesting sand during take-off on unimproved runway Inset: Gas turbine engine vanes with molten CMAS deposits, (b) NAVY V-22 rotorcraft performing landing maneuver under severe ‘brown-out’ heavy dust/sand conditions, (c) Dust storm across the Red Sea May 13, 2005, (d) A plane passing through a cloud of volcanic ash, and (e) Volcanic ash deposited on aircraft. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 3 (a) C-17 military aircraft ingesting sand during take-off on unimproved runway Inset: Gas turbine engine vanes with molten CMAS deposits, (b) NAVY V-22 rotorcraft performing landing maneuver under severe ‘brown-out’ heavy dust/sand conditions, (c) Dust storm across the Red Sea May 13, 2005, (d) A plane passing through a cloud of volcanic ash, and (e) Volcanic ash deposited on aircraft. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [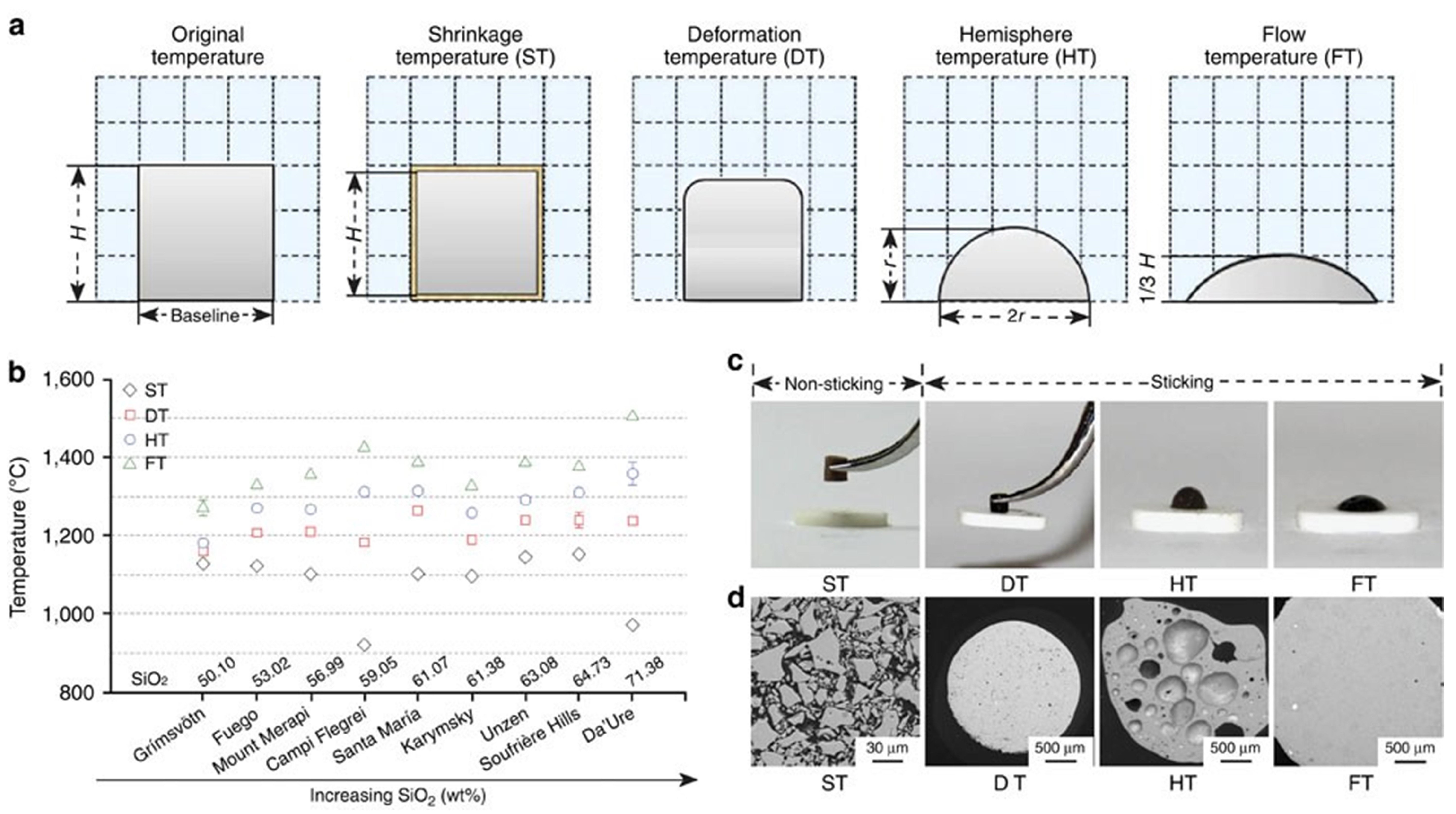 Fig. 10 (a) Schematic diagram of the volcanic ash melting process; (b) Transition temperatures of volcanic ash with different compositions at various stages; (c) Photographs of volcanic ash at different melting stages; (d) Backscattered electron images of volcanic ash at various melting stages. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 10 (a) Schematic diagram of the volcanic ash melting process; (b) Transition temperatures of volcanic ash with different compositions at various stages; (c) Photographs of volcanic ash at different melting stages; (d) Backscattered electron images of volcanic ash at various melting stages. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [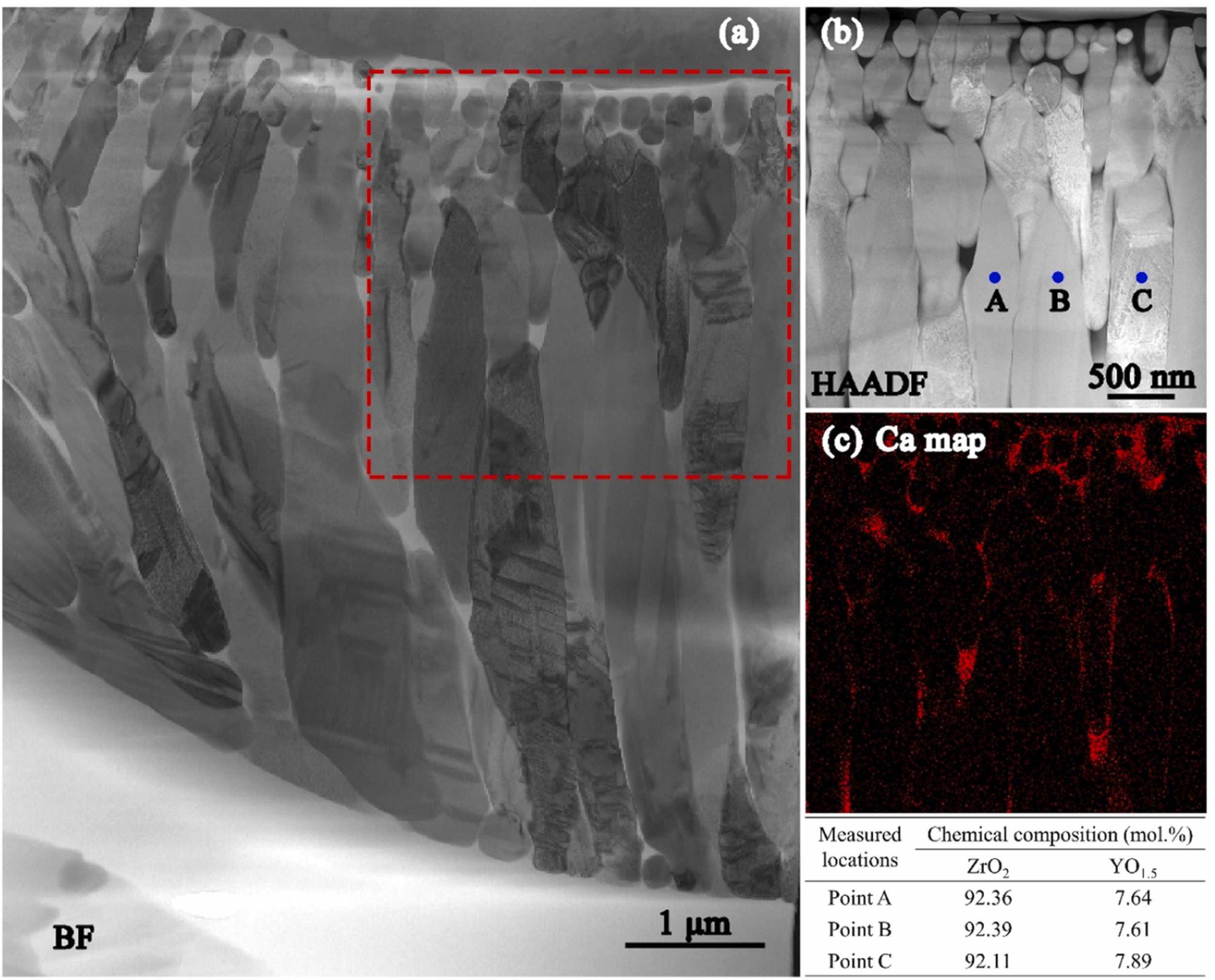 Fig 16. (a) Bright-field TEM image of CMAS infiltration front at 1250 ℃ for 2 h in 8YSZ TBC, (b-c) HAADF image, and the corresponding Ca mapping of the dashed rectangle area in (a). The table at the bottom right lists the chemical compositions of points A, B, and C in (b). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig 16. (a) Bright-field TEM image of CMAS infiltration front at 1250 ℃ for 2 h in 8YSZ TBC, (b-c) HAADF image, and the corresponding Ca mapping of the dashed rectangle area in (a). The table at the bottom right lists the chemical compositions of points A, B, and C in (b). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [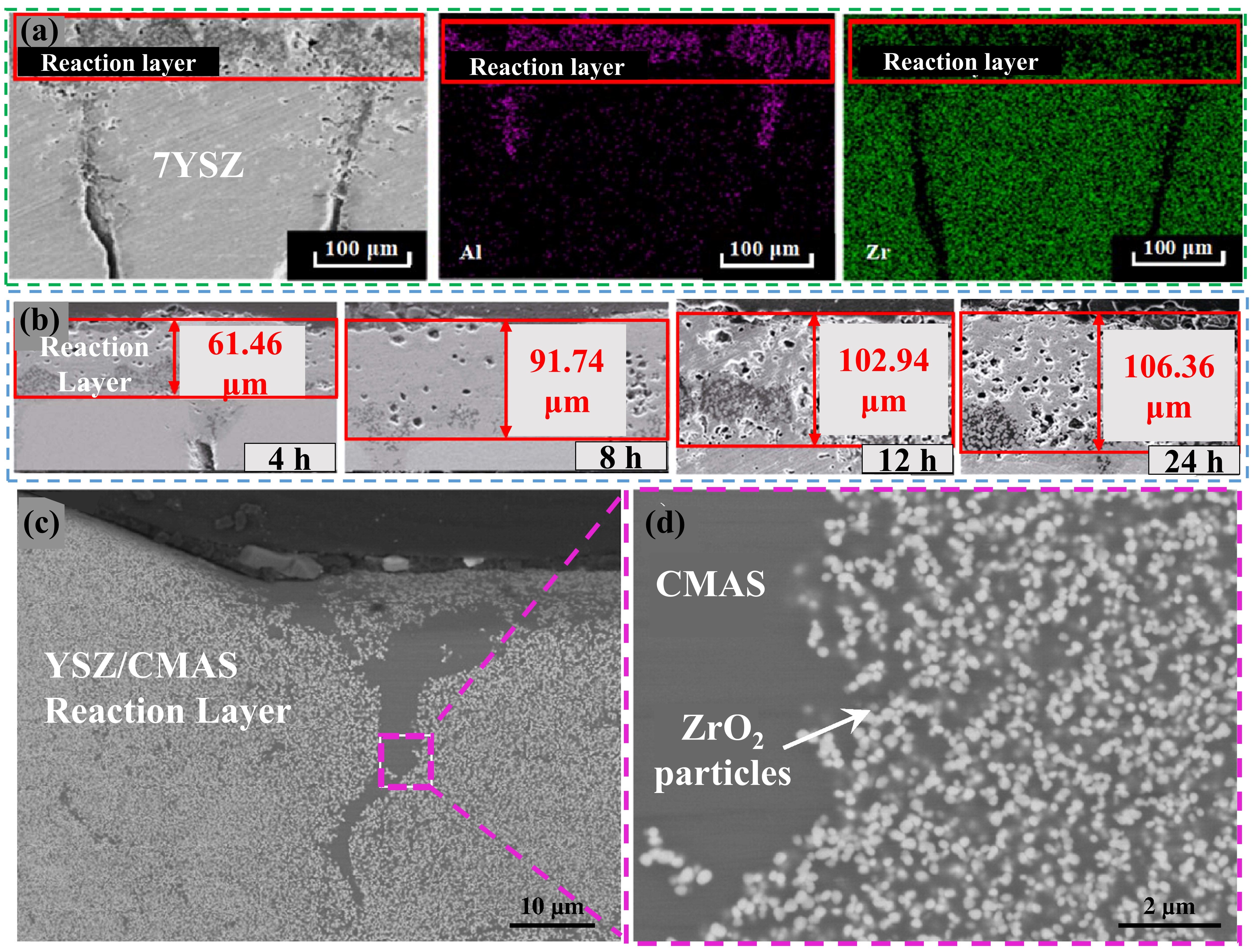 Fig. 17. (a) SEM and EDS images of the interaction layer on cross-section, (b) the thickness of the reaction layer at different holding times, and (c-d) cross-section of the CMAS/YSZ interaction zone in the dissolution/reprecipitation process. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 17. (a) SEM and EDS images of the interaction layer on cross-section, (b) the thickness of the reaction layer at different holding times, and (c-d) cross-section of the CMAS/YSZ interaction zone in the dissolution/reprecipitation process. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [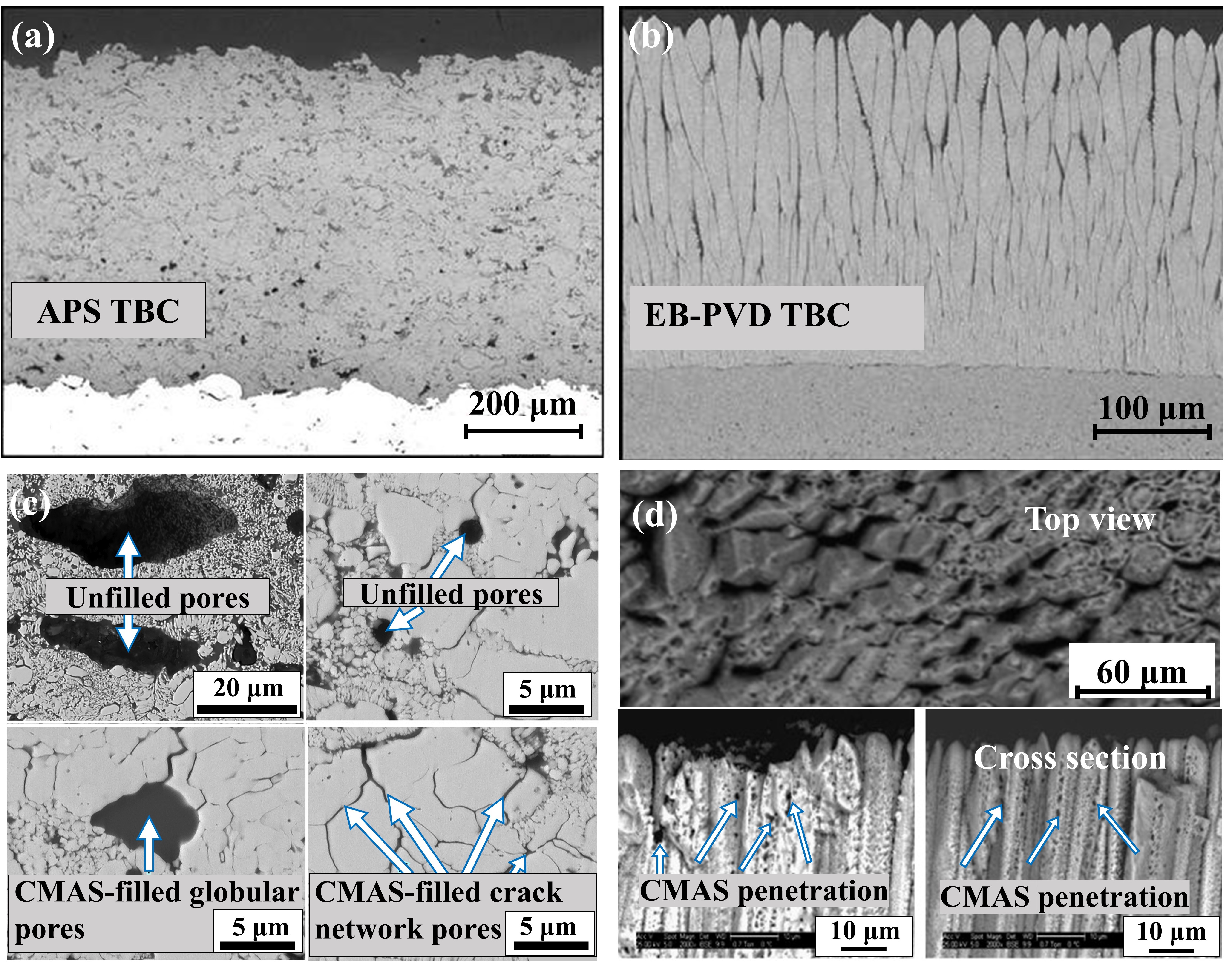 Fig. 18. Typical microstructure and the microstructure after CMAS of TBC prepared by APS and EB-PVD: (a) 7YSZ TBC prepared by APS and (b) EB-PVD, (c) microstructures of 8YSZ APS TBC after CMAS corrosion at 1250 ℃ for 3 h and (d) microstructures of 7YSZ EB-PVD TBC after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 4 h. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 18. Typical microstructure and the microstructure after CMAS of TBC prepared by APS and EB-PVD: (a) 7YSZ TBC prepared by APS and (b) EB-PVD, (c) microstructures of 8YSZ APS TBC after CMAS corrosion at 1250 ℃ for 3 h and (d) microstructures of 7YSZ EB-PVD TBC after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 4 h. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [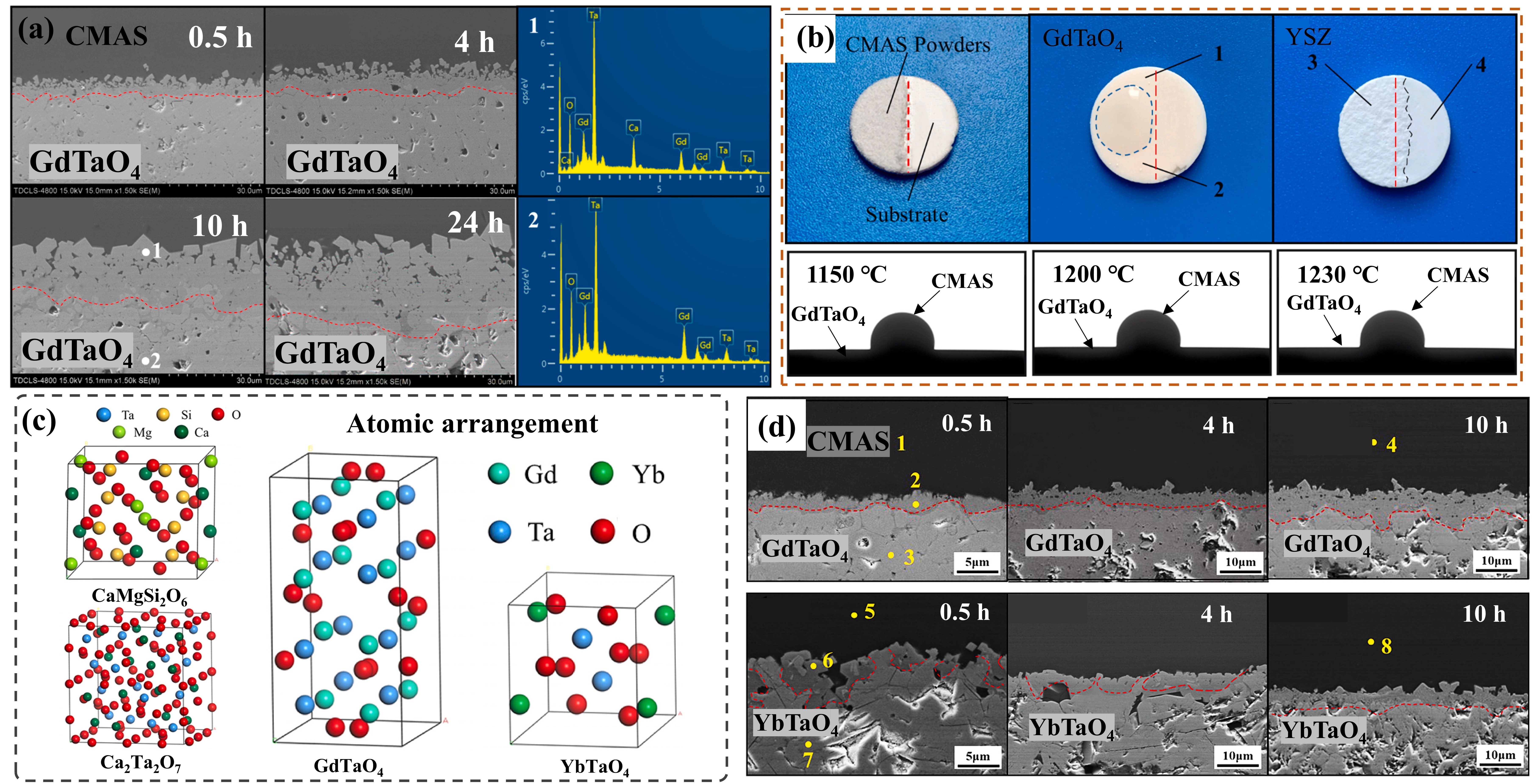 Fig. 22. The interface microstructure, wetting process on-line photographs and atomic arrangement of GdTaO4 and YbTaO4: (a) the interface microstructure of GdTaO4 and CMAS (33Ca-9Mg-13Al-45Si) at 1350 ℃ for different time, (b) the surface state of GdTaO4 and YSZ before and after high-temperature reaction, (c) the atomic arrangement of CaMgSi2O6, Ca2Ta2O7, GdTaO4 and YbTaO4 and (d) images of the reaction interface between residual CMAS and substrate. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 22. The interface microstructure, wetting process on-line photographs and atomic arrangement of GdTaO4 and YbTaO4: (a) the interface microstructure of GdTaO4 and CMAS (33Ca-9Mg-13Al-45Si) at 1350 ℃ for different time, (b) the surface state of GdTaO4 and YSZ before and after high-temperature reaction, (c) the atomic arrangement of CaMgSi2O6, Ca2Ta2O7, GdTaO4 and YbTaO4 and (d) images of the reaction interface between residual CMAS and substrate. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [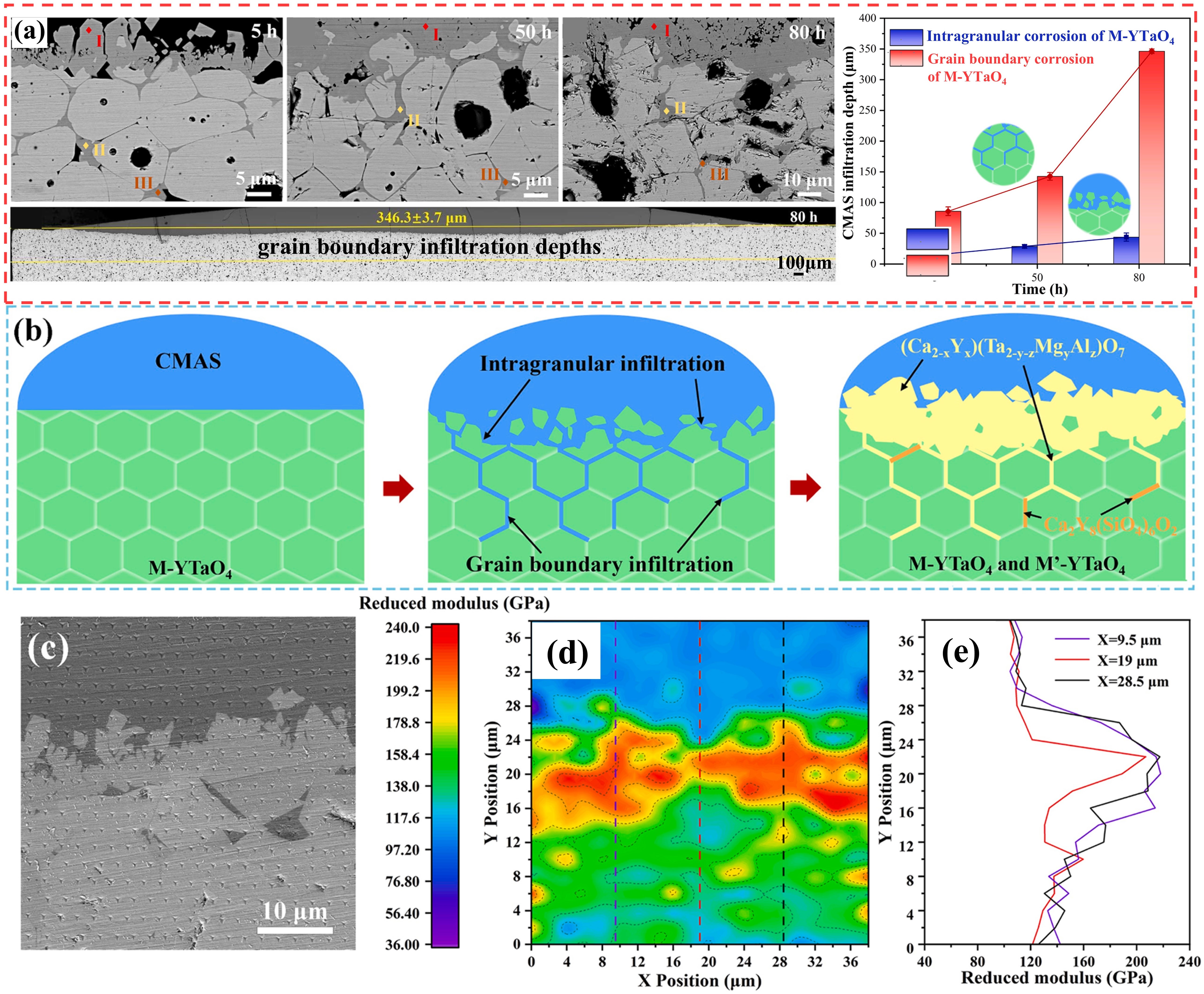 Fig. 23. Corrosion mechanism of M-YTaO4: (a) images of cross-sections and grain boundary infiltration depths of M-YTaO4 after CMAS corrosion, (b) schematic diagram of CMAS corrosion of M-YTaO4, (c) the interface between residual CMAS melt and M-YTaO4 substrate after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 5 h, (d) Mapping and (e) section lines of reduced moduli corresponding to (c). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 23. Corrosion mechanism of M-YTaO4: (a) images of cross-sections and grain boundary infiltration depths of M-YTaO4 after CMAS corrosion, (b) schematic diagram of CMAS corrosion of M-YTaO4, (c) the interface between residual CMAS melt and M-YTaO4 substrate after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 5 h, (d) Mapping and (e) section lines of reduced moduli corresponding to (c). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [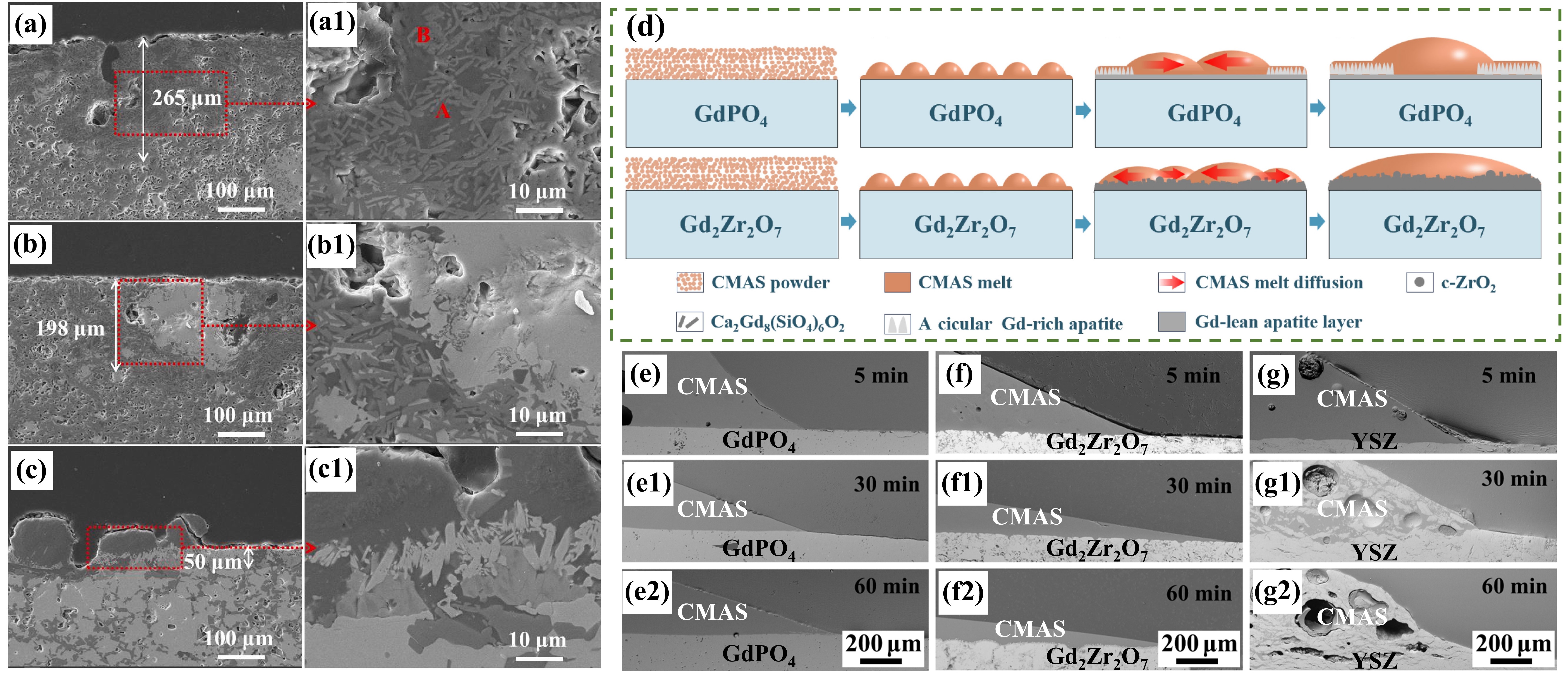 Fig. 24. (a-c) SEM images of the cross-sectional morphologies of LMA/GdPO4 after CMAS corrosion, (d) Schematic diagrams of CMAS wetting behavior of GdPO4 and Gd2Zr2O7, and cross-sectional images of contact angles of CMAS droplets on (e-e2) GdPO4, (f-f2) Gd2Zr2O7, and (g-g2) YSZ. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 24. (a-c) SEM images of the cross-sectional morphologies of LMA/GdPO4 after CMAS corrosion, (d) Schematic diagrams of CMAS wetting behavior of GdPO4 and Gd2Zr2O7, and cross-sectional images of contact angles of CMAS droplets on (e-e2) GdPO4, (f-f2) Gd2Zr2O7, and (g-g2) YSZ. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [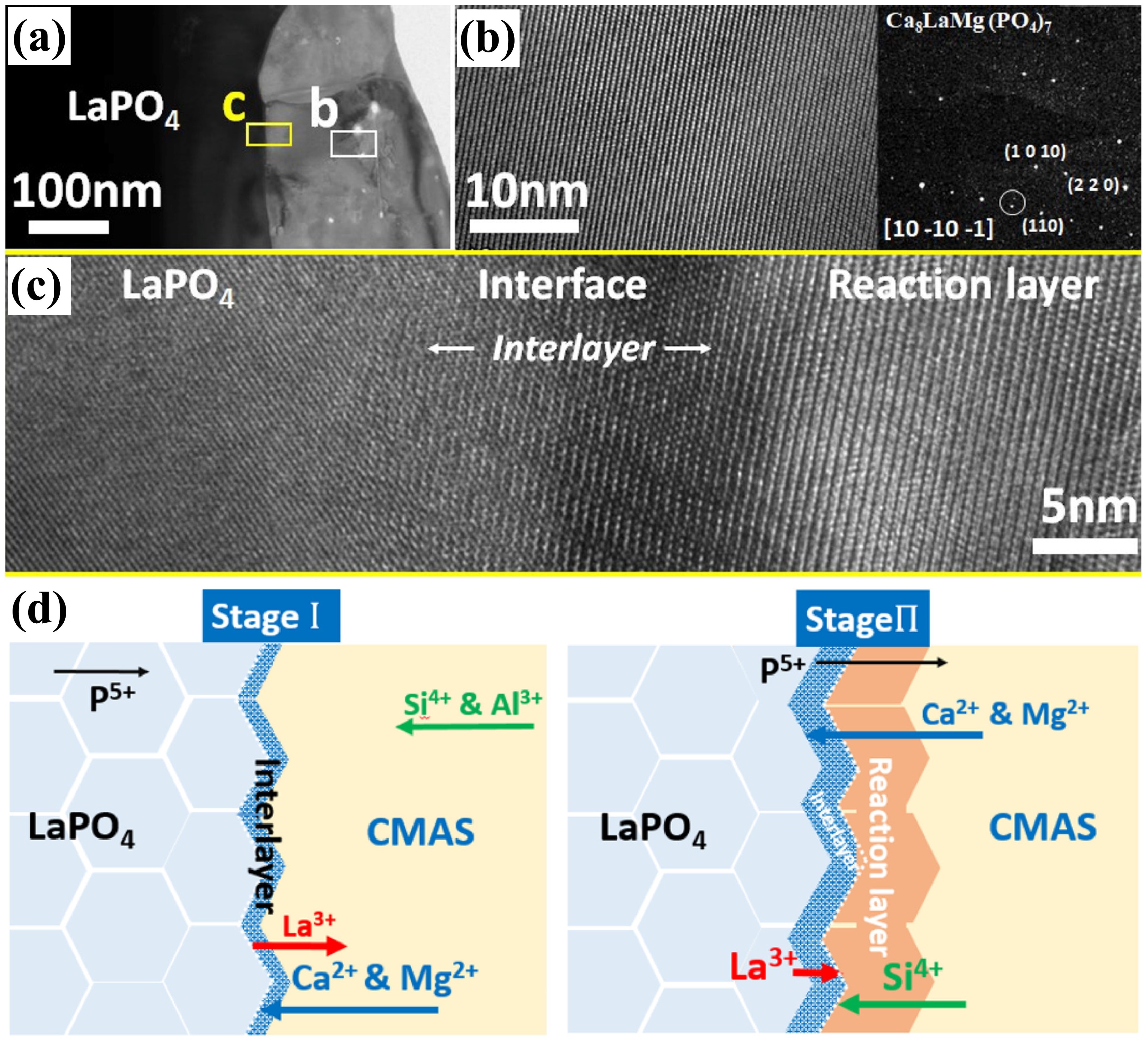 Fig. 25. (a) Bright-field TEM image of LaPO4 and its reaction layer with CMAS after CMAS attack at 1250 ℃ for 5min, (b) HRTEM image of the reaction layer in (a), with an inset image of the diffraction pattern of the reaction layer, (c) HRTEM image of interlayer, and (d) schematic of the transport mechanisms associated with the formation of a transient interlayer and reaction layer across the LaPO4-CMAS interface when exposed to CMAS attack at 1250 ℃. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 25. (a) Bright-field TEM image of LaPO4 and its reaction layer with CMAS after CMAS attack at 1250 ℃ for 5min, (b) HRTEM image of the reaction layer in (a), with an inset image of the diffraction pattern of the reaction layer, (c) HRTEM image of interlayer, and (d) schematic of the transport mechanisms associated with the formation of a transient interlayer and reaction layer across the LaPO4-CMAS interface when exposed to CMAS attack at 1250 ℃. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [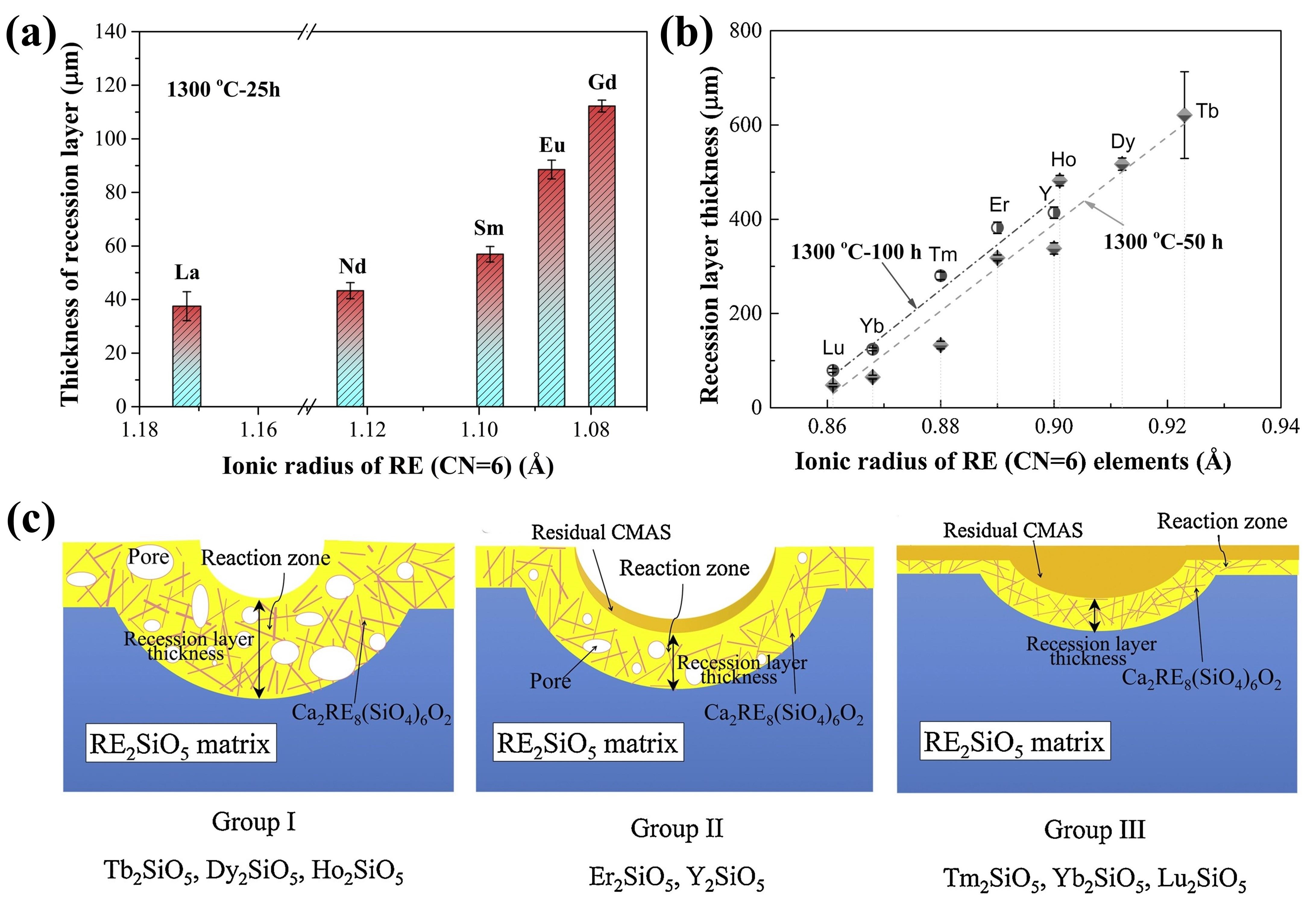 Fig. 28 (a) The recession layer thickness of X1-RE2SiO5 (RE = La, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd) after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 25 h; (b) The recession layer thickness of X2- RE2SiO5 (RE = Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Y, Tm, Yb, and Lu) after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃for 50 h and 100 h; (c) Schematic diagram of CMAS corrosion of X2-RE2SiO5 at 1300 ℃. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 28 (a) The recession layer thickness of X1-RE2SiO5 (RE = La, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd) after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for 25 h; (b) The recession layer thickness of X2- RE2SiO5 (RE = Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Y, Tm, Yb, and Lu) after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃for 50 h and 100 h; (c) Schematic diagram of CMAS corrosion of X2-RE2SiO5 at 1300 ℃. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [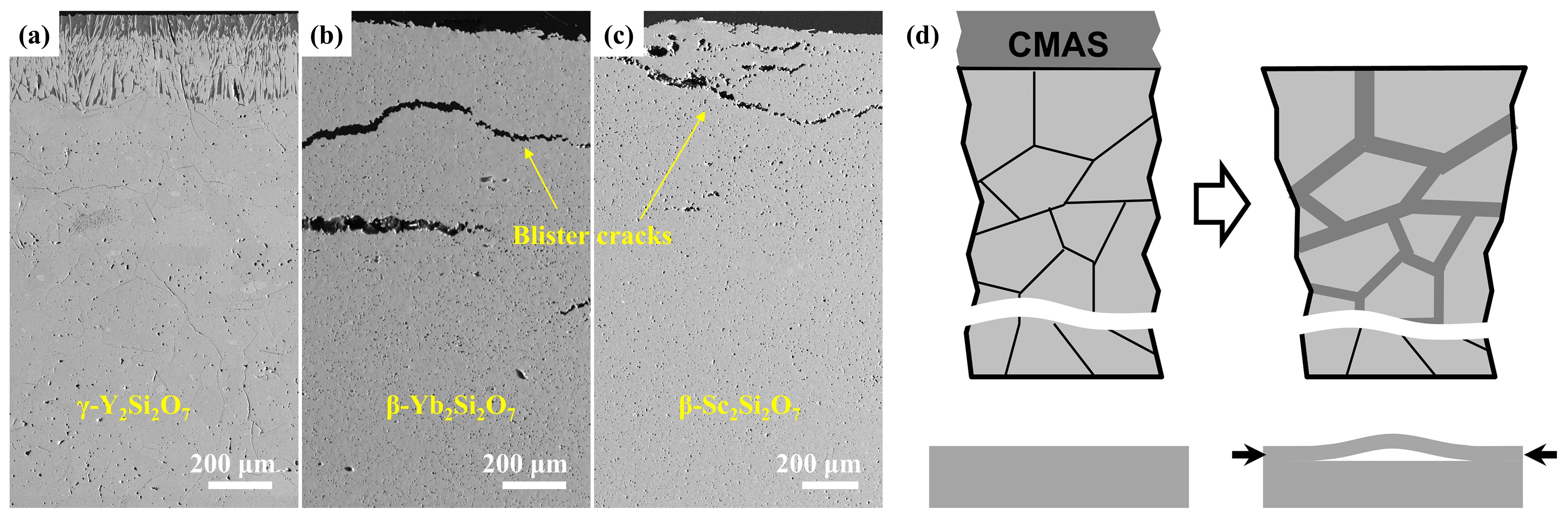 Fig. 36 (a-c) Cross-sectional morphology of γ-Y2Si2O7, β-Yb2Si2O7, and β-Sc2Si2O7 after CMAS corrosion at 1500 ℃; (d) Schematic diagram of the formation of “blister” cracks. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 36 (a-c) Cross-sectional morphology of γ-Y2Si2O7, β-Yb2Si2O7, and β-Sc2Si2O7 after CMAS corrosion at 1500 ℃; (d) Schematic diagram of the formation of “blister” cracks. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [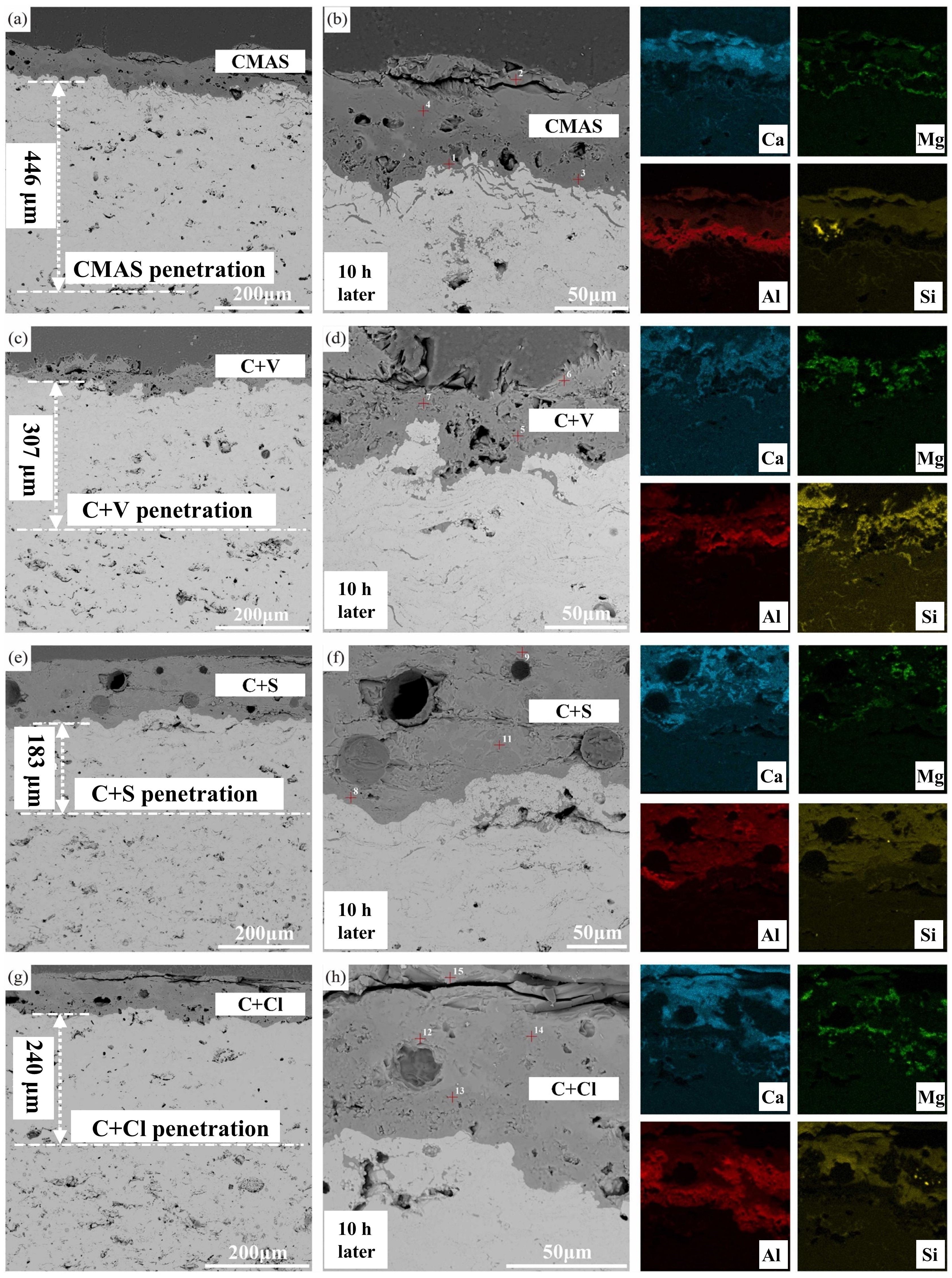 Fig. 39 A cross-sectional SEM images of the Al2O3-YSZ coating exposed to (a-b) CMAS, (c-d) CMAS+NaVO3 powders, (e-f) CMAS+Na2SO4 powders, and (g-h) CMAS+NaCl powders for 10 h, and corresponding EDS mapping results (Ca, Mg, Al, and Si elements) are also provided. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 39 A cross-sectional SEM images of the Al2O3-YSZ coating exposed to (a-b) CMAS, (c-d) CMAS+NaVO3 powders, (e-f) CMAS+Na2SO4 powders, and (g-h) CMAS+NaCl powders for 10 h, and corresponding EDS mapping results (Ca, Mg, Al, and Si elements) are also provided. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [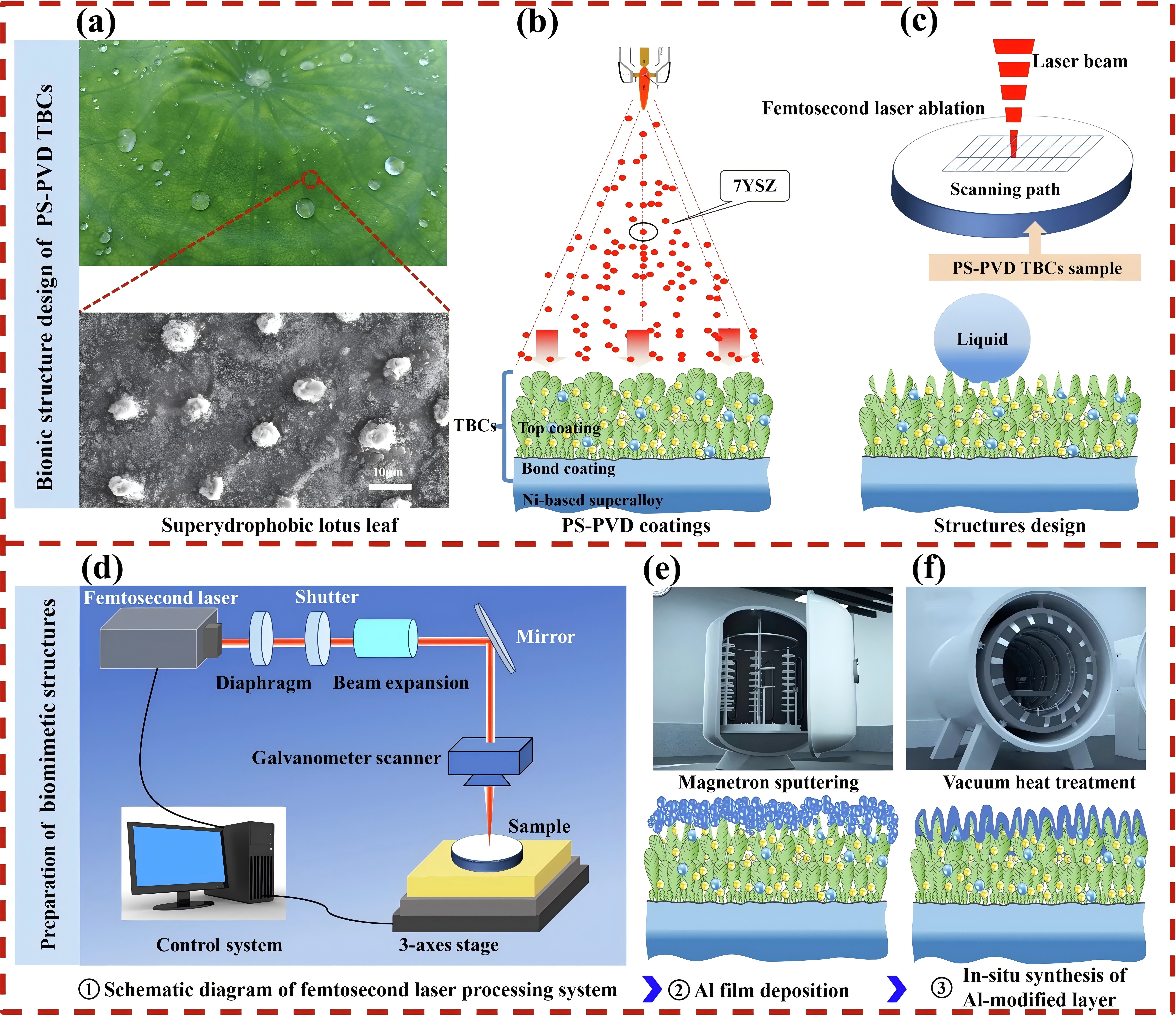 Fig. 40 (a) Superhydrophobic lotus leaf and its microstructure-the source of inspiration. (b) PS-PVD TBCs preparation. (c) Constructing the lotus leaf structure on PS-PVD TBCs surface. (d) Schematic diagram of femtosecond laser processing system and fabrication of micro-nanostructured PS-PVD TBCs. (e) Al film deposition by magnetron sputtering. (f) In situ synthesis of Al-modified layer on laser textured PS-PVD TBCs by vacuum heat treatment. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 40 (a) Superhydrophobic lotus leaf and its microstructure-the source of inspiration. (b) PS-PVD TBCs preparation. (c) Constructing the lotus leaf structure on PS-PVD TBCs surface. (d) Schematic diagram of femtosecond laser processing system and fabrication of micro-nanostructured PS-PVD TBCs. (e) Al film deposition by magnetron sputtering. (f) In situ synthesis of Al-modified layer on laser textured PS-PVD TBCs by vacuum heat treatment. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [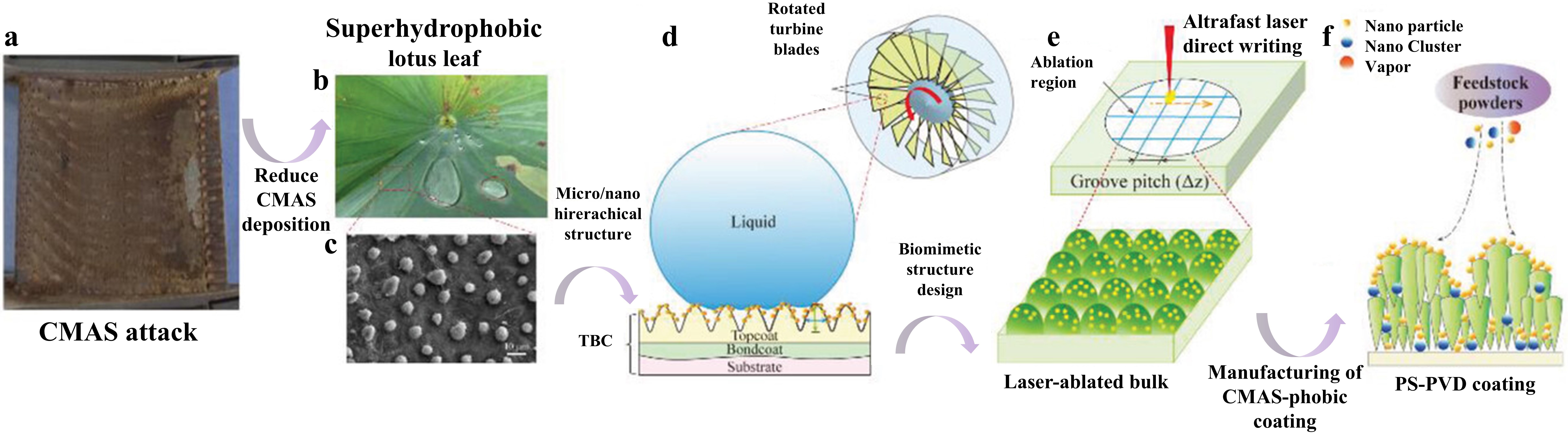 Fig. 41 (a) Volcanic ash accumulation on turbine blades leading to engine failure. (b) Lotus leaf-inspired superhydrophobicity for CMAS-phobic surface design. (c) Micro/nano hierarchical structure on TBC surface reducing CMAS deposition. (d) Biomimetic structure application on turbine blades to prevent CMAS adherence. (e) Ultrafast laser direct writing for micro/nano hierarchical structure on (Gd0.9Yb0.1)2Zr2O7 material. (f) PS-PVD process for CMAS-phobic coating with microconical papillae and nanoparticles. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 41 (a) Volcanic ash accumulation on turbine blades leading to engine failure. (b) Lotus leaf-inspired superhydrophobicity for CMAS-phobic surface design. (c) Micro/nano hierarchical structure on TBC surface reducing CMAS deposition. (d) Biomimetic structure application on turbine blades to prevent CMAS adherence. (e) Ultrafast laser direct writing for micro/nano hierarchical structure on (Gd0.9Yb0.1)2Zr2O7 material. (f) PS-PVD process for CMAS-phobic coating with microconical papillae and nanoparticles. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [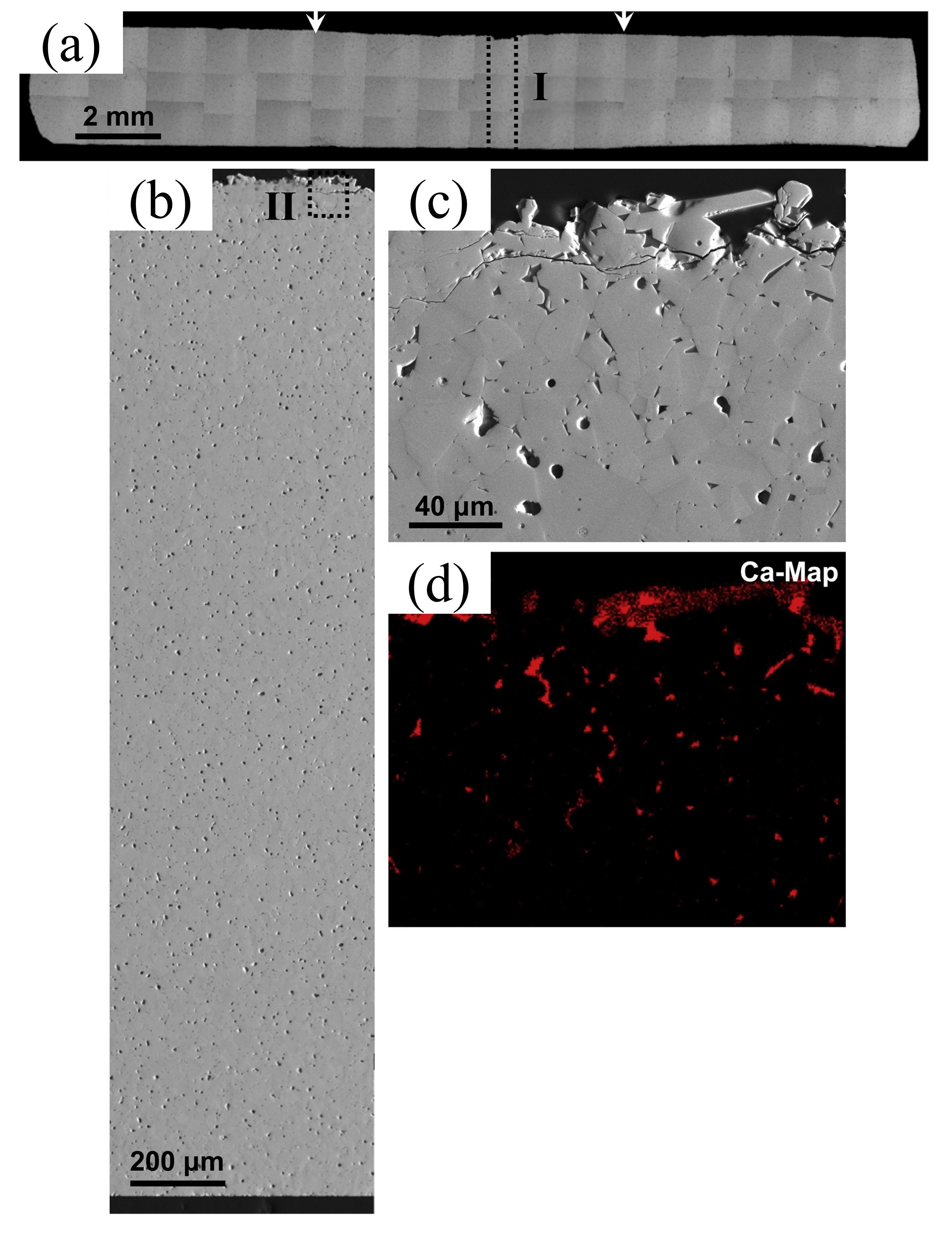 Fig. 43 (a) Collage of cross-sectional optical micrographs of β-Yb2Si2O7/1 vol% CMAS pellet that have interacted with CMAS at 1500 ℃ for 24 h. The region between the arrows is where the CMAS was applied. (b) Cross-sectional SEM image of the whole pellet from the region I. (c) Higher-magnification cross-sectional SEM image of the region II, and (d) corresponding EDS elemental Ca map. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
Fig. 43 (a) Collage of cross-sectional optical micrographs of β-Yb2Si2O7/1 vol% CMAS pellet that have interacted with CMAS at 1500 ℃ for 24 h. The region between the arrows is where the CMAS was applied. (b) Cross-sectional SEM image of the whole pellet from the region I. (c) Higher-magnification cross-sectional SEM image of the region II, and (d) corresponding EDS elemental Ca map. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [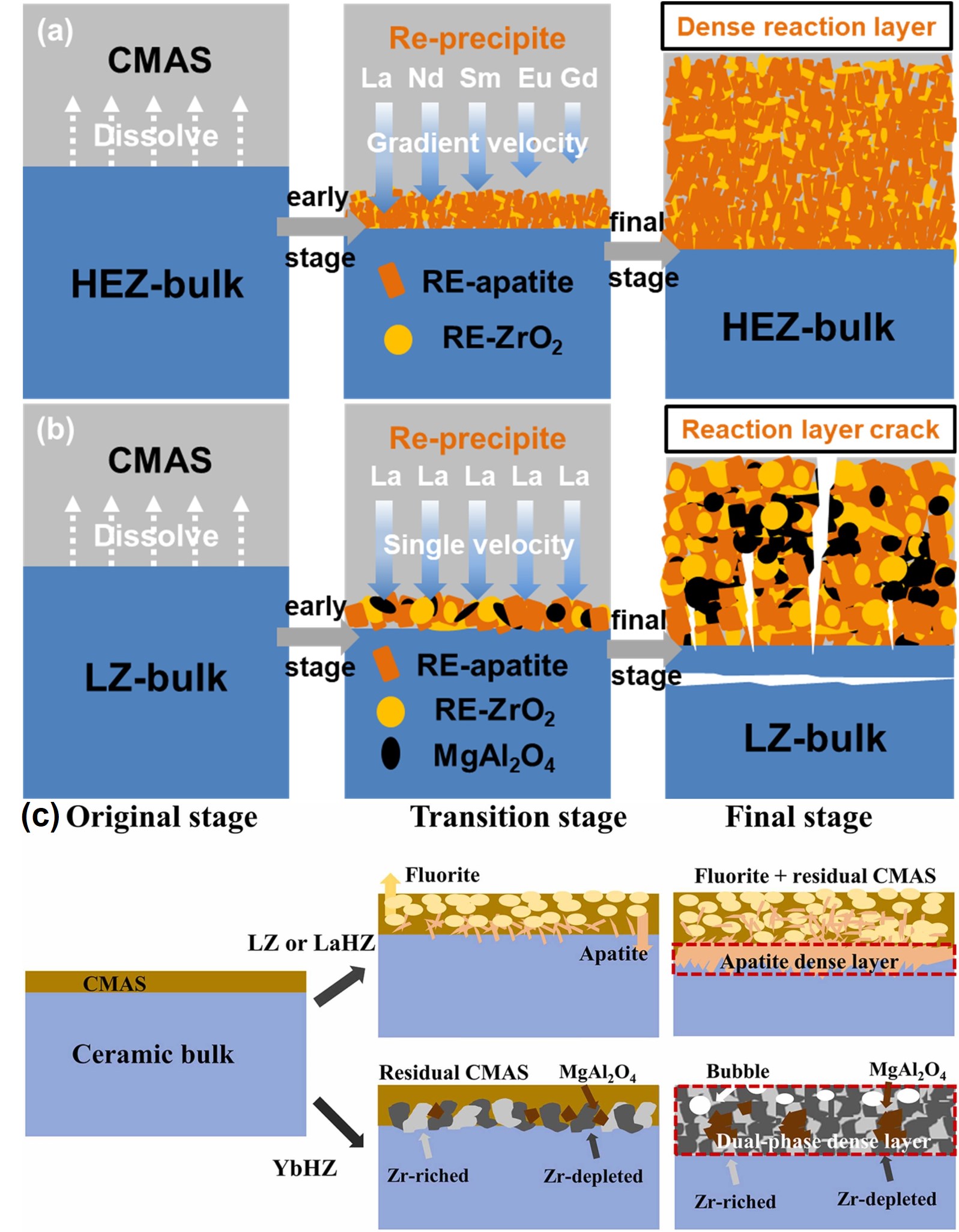 Fig. 46 CMAS-induced corrosion in HEZ and LZ ceramics. (a) HEZ: Dense RE-apatite and RE-ZrO2 layer without cracks, exhibiting graceful degradation. (b) LZ: Formation of RE-apatite, RE-ZrO2, and MgAl2O4 layer with cracks, indicating reduced CMAS resistance. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [
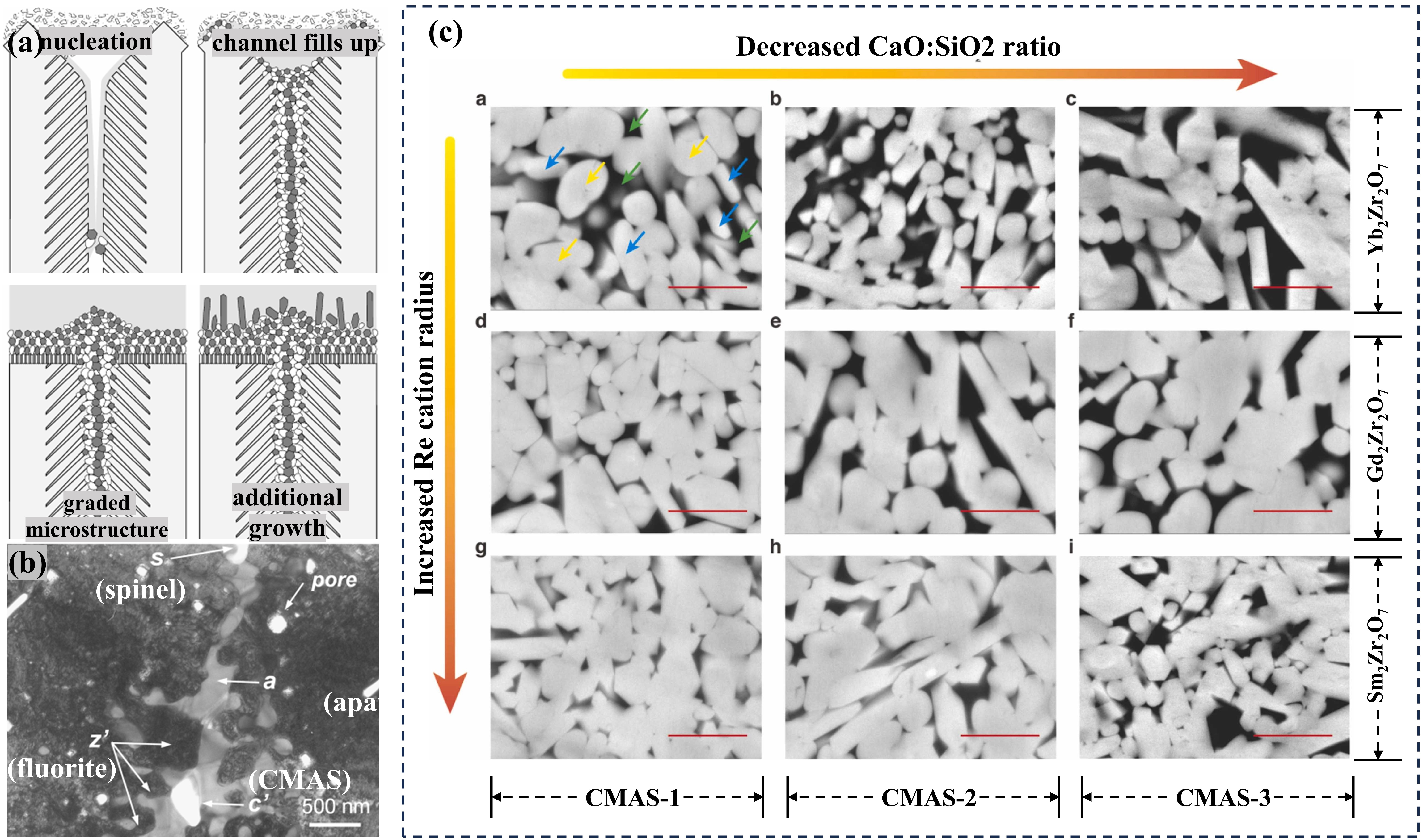
Fig. 46 CMAS-induced corrosion in HEZ and LZ ceramics. (a) HEZ: Dense RE-apatite and RE-ZrO2 layer without cracks, exhibiting graceful degradation. (b) LZ: Formation of RE-apatite, RE-ZrO2, and MgAl2O4 layer with cracks, indicating reduced CMAS resistance. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [