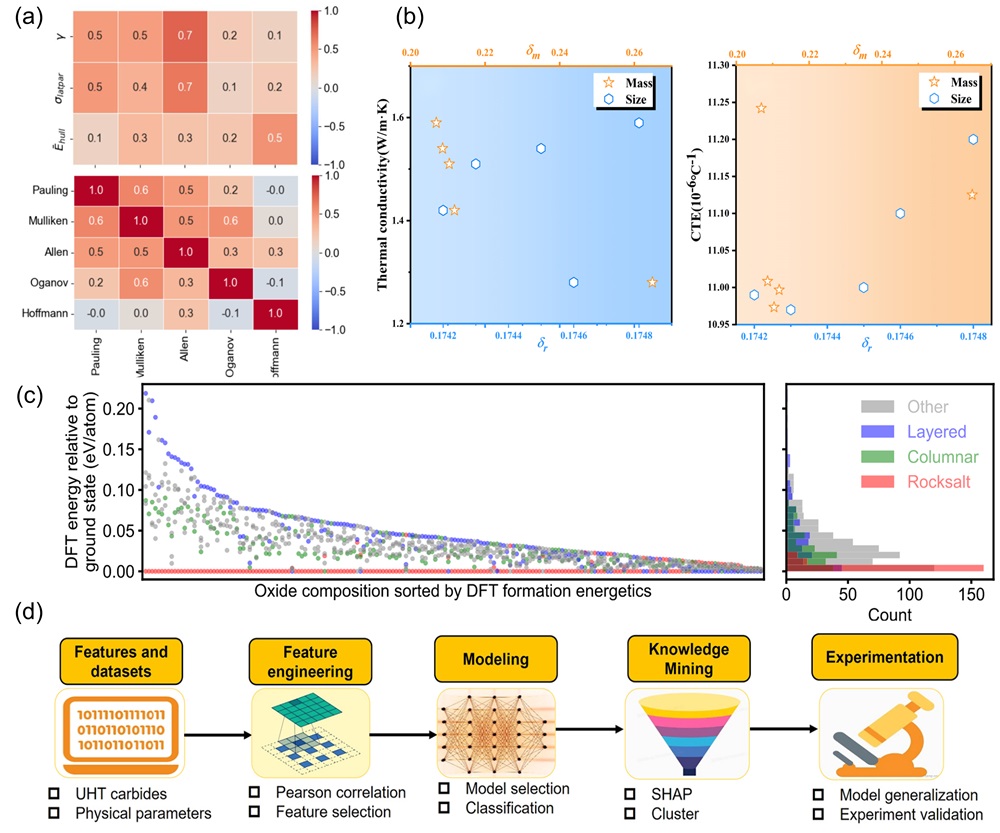
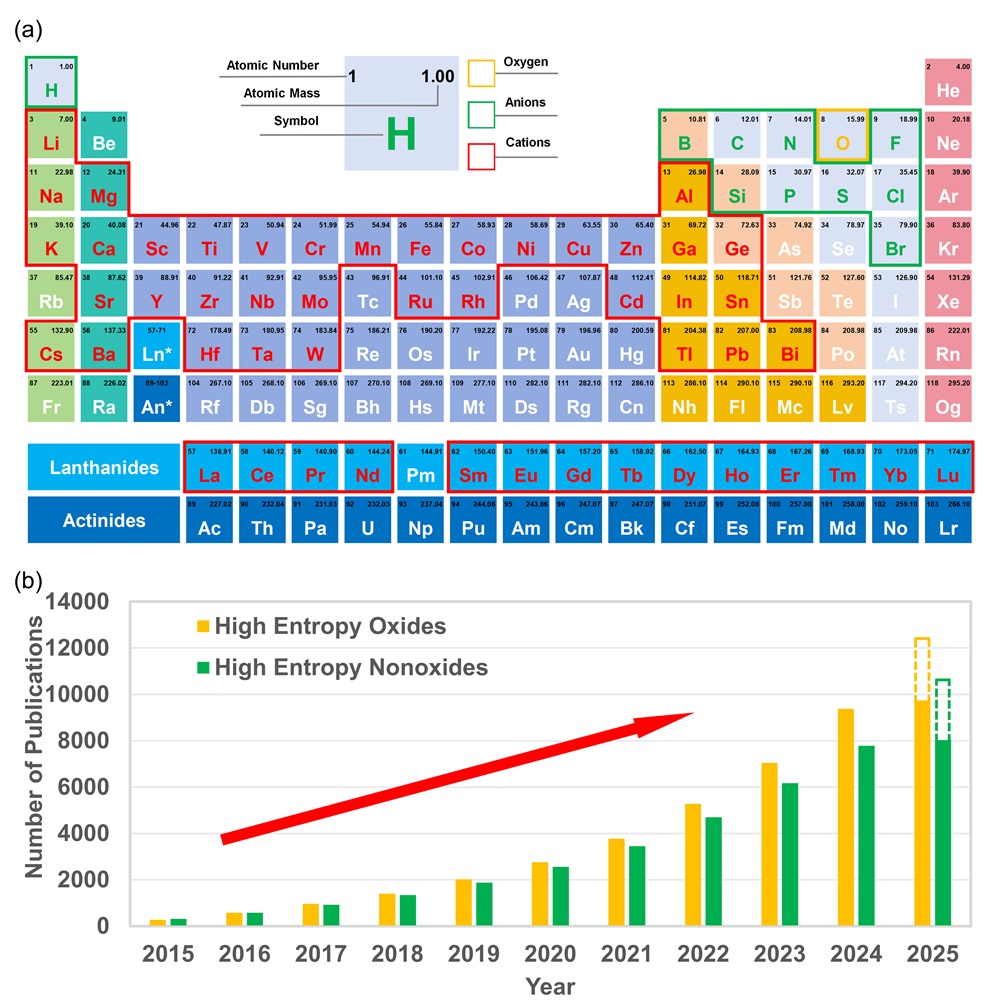
 Fig. 1. (b) All the constituent elements reported in HECs to date. (b) Total number of publications on major HECs over the last decade. Data was retrieved from Web of Science on February 28, 2025, using keywords: “high-entropy”, “oxide”, “boride”, “carbide”, “nitride”, “silicide”, “fluoride”, “hydride”, “phosphide”, “sulfide”, and “ceramics”.
Fig. 1. (b) All the constituent elements reported in HECs to date. (b) Total number of publications on major HECs over the last decade. Data was retrieved from Web of Science on February 28, 2025, using keywords: “high-entropy”, “oxide”, “boride”, “carbide”, “nitride”, “silicide”, “fluoride”, “hydride”, “phosphide”, “sulfide”, and “ceramics”.
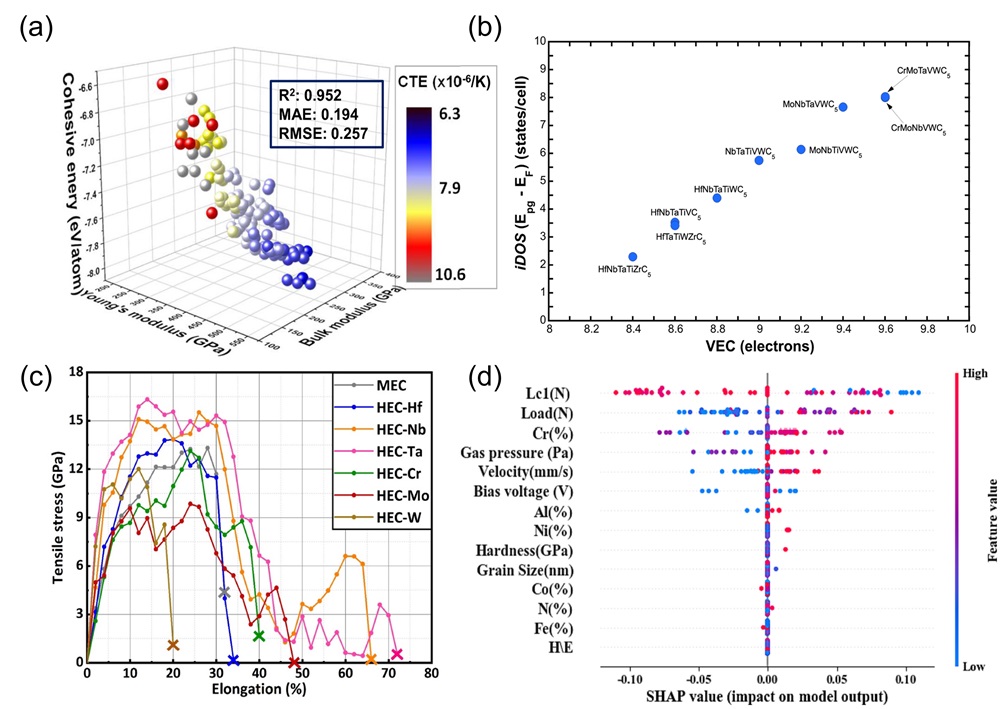 Fig. 3. (a) The 3D plots of the NET (neural network) training set were generated based on three parameters (bulk modulus, Young's modulus, and cohesive energy) [
Fig. 3. (a) The 3D plots of the NET (neural network) training set were generated based on three parameters (bulk modulus, Young's modulus, and cohesive energy) [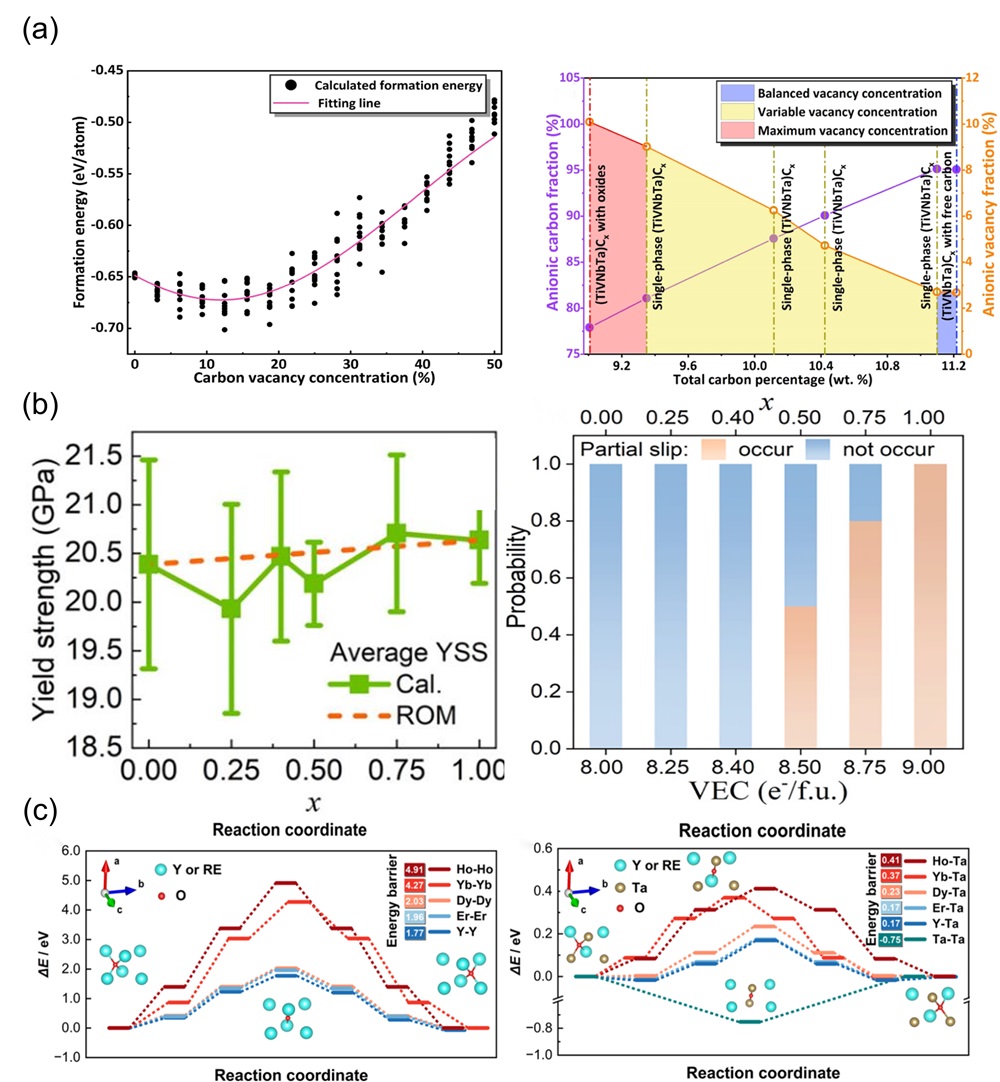 Fig. 4. (a) The fitting formation energy curve of (TiVNbTa)Cx with variation of anionic vacancy concentration; Curves of anionic carbon and vacancy fraction under changing carbon content [
Fig. 4. (a) The fitting formation energy curve of (TiVNbTa)Cx with variation of anionic vacancy concentration; Curves of anionic carbon and vacancy fraction under changing carbon content [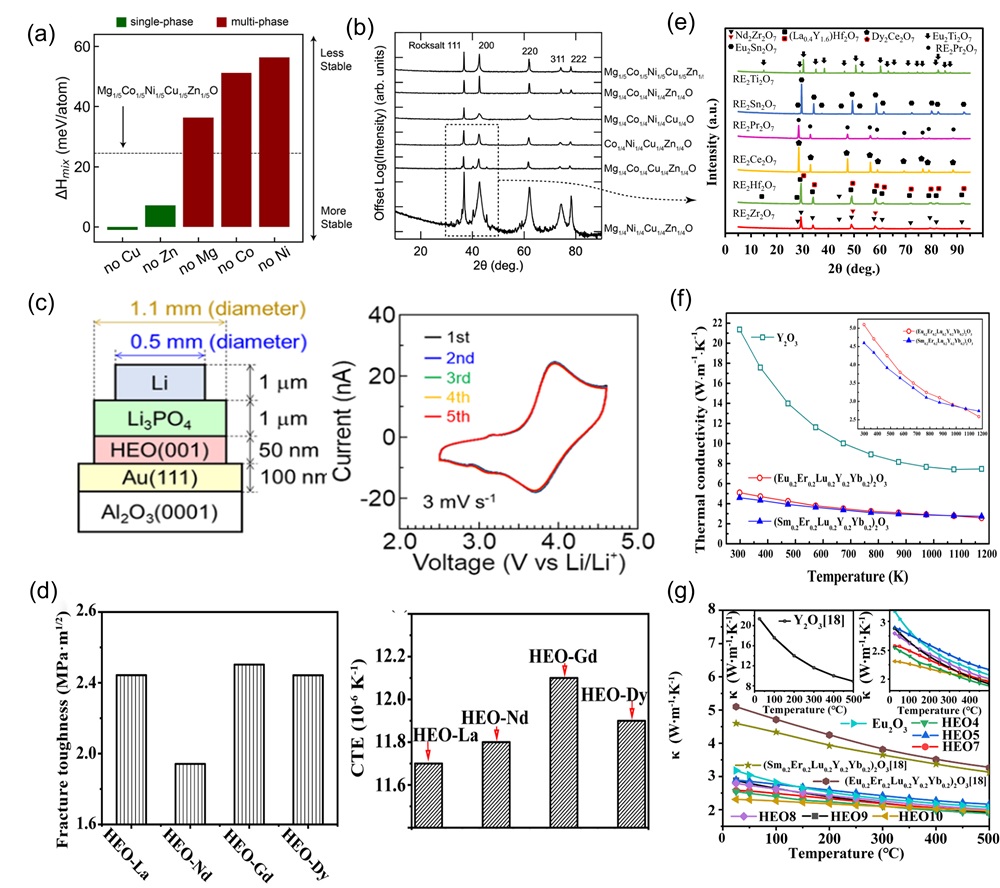 Fig. 6. (a) X-ray diffractograms of four-component derivatives of (MgCoNiCuZn)O as a substrate; (b) DFT analysis of four diffractive phase compositions by mixing enthalpy [
Fig. 6. (a) X-ray diffractograms of four-component derivatives of (MgCoNiCuZn)O as a substrate; (b) DFT analysis of four diffractive phase compositions by mixing enthalpy [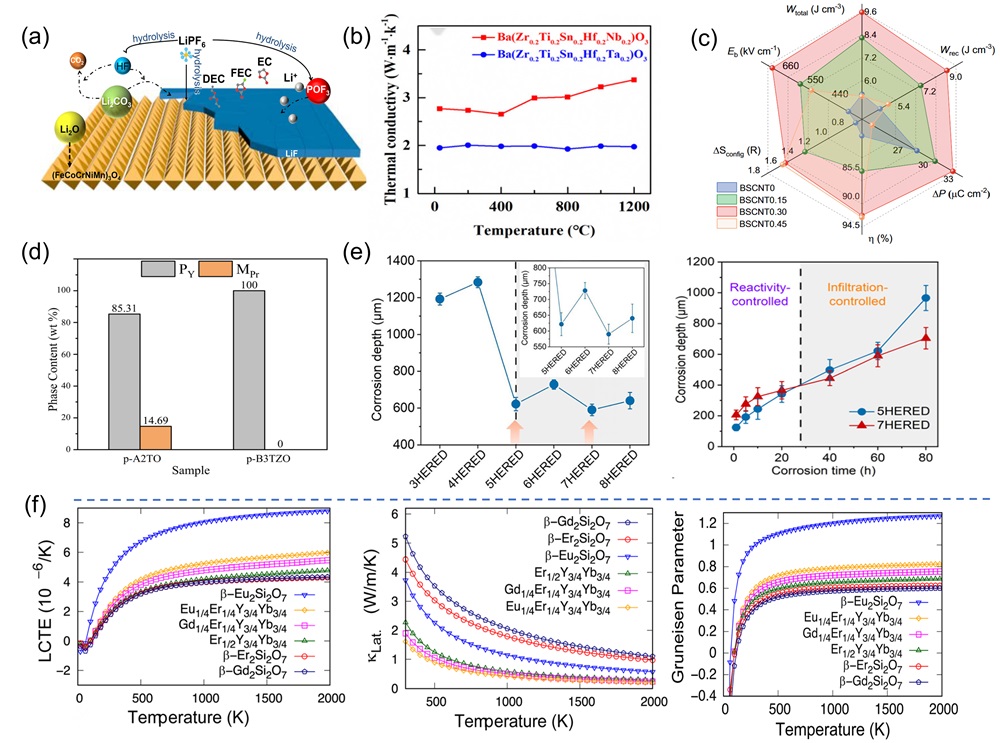 Fig. 7. (a) Schematic diagram representation of the conversion of Li2O, LiF, and Li2CO3 during the cycling process of the preconditioned HEOs [
Fig. 7. (a) Schematic diagram representation of the conversion of Li2O, LiF, and Li2CO3 during the cycling process of the preconditioned HEOs [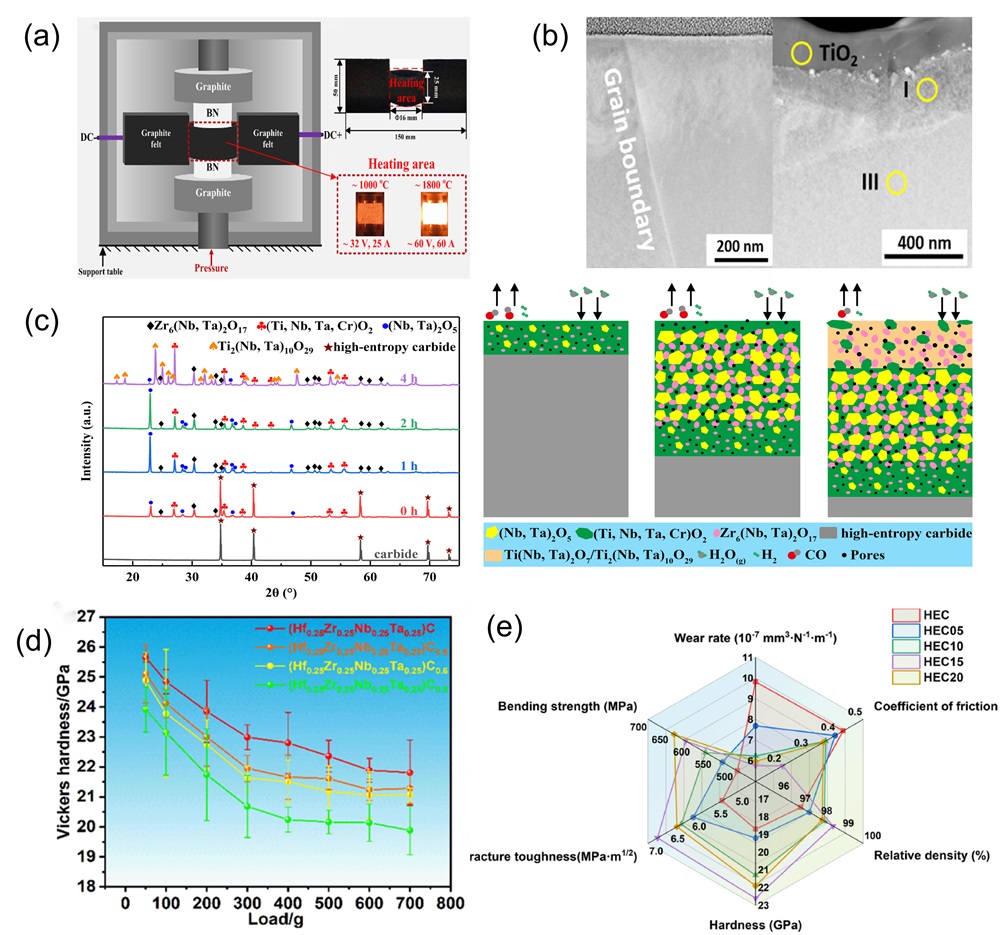 Fig. 8. (a) Schematic diagram of ultra-fast pressure sintering apparatus [
Fig. 8. (a) Schematic diagram of ultra-fast pressure sintering apparatus [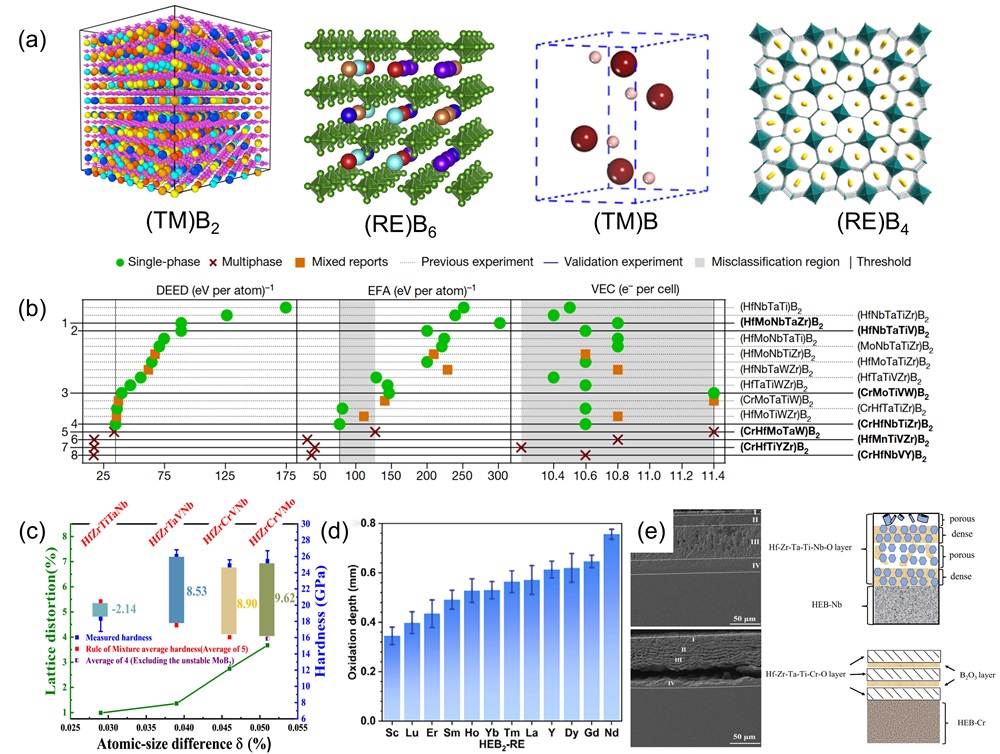 Fig. 9. (a) Crystal structures of different HEBs [
Fig. 9. (a) Crystal structures of different HEBs [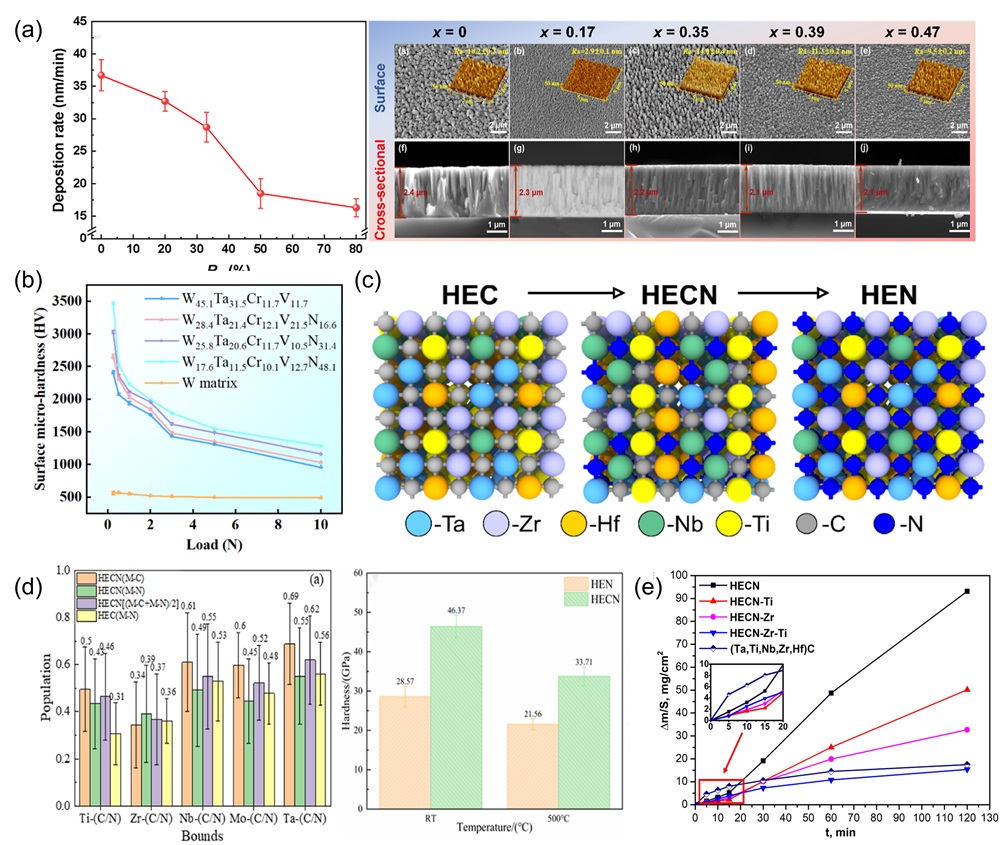 Fig. 10. (a) SEM images of surface and cross-sectional morphology of (MoNbTaTiZr)1-xNx coatings under different x; Deposition rates of (MoNbTaTiZr)1-xNx coatings with different RN [
Fig. 10. (a) SEM images of surface and cross-sectional morphology of (MoNbTaTiZr)1-xNx coatings under different x; Deposition rates of (MoNbTaTiZr)1-xNx coatings with different RN [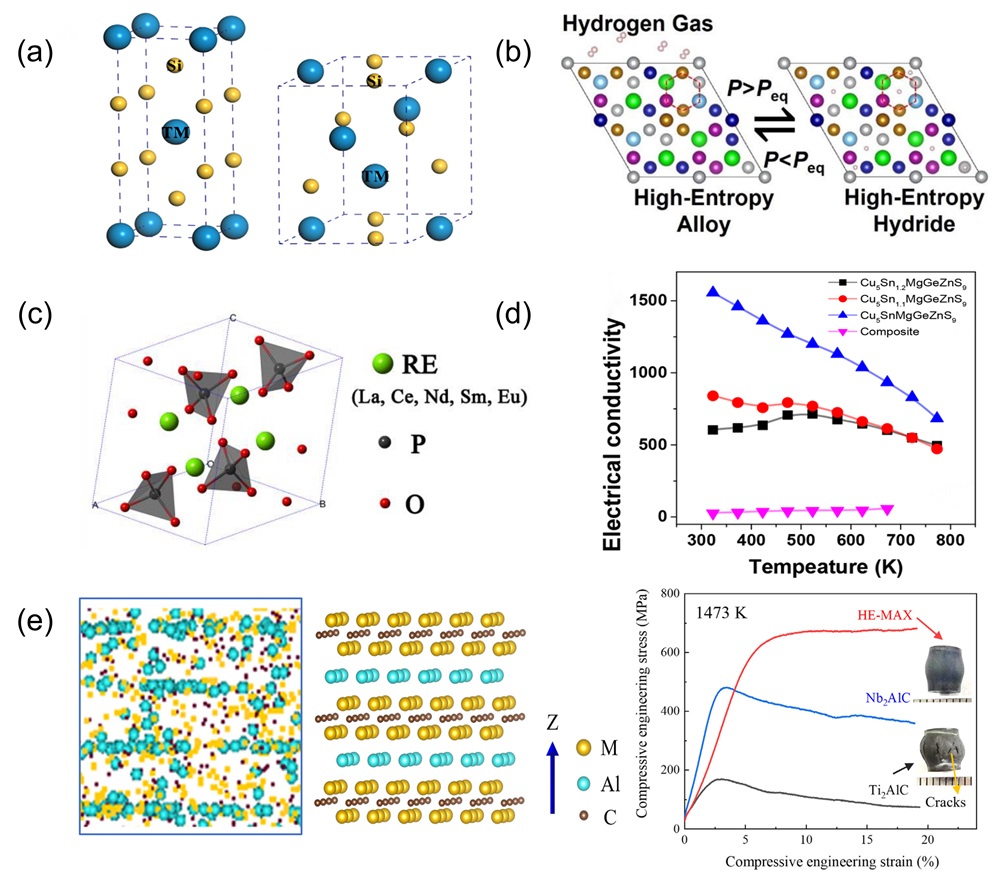 Fig. 11. (a) Crystal structure of tetragonal transition metal disilicide (left), hexagonal transition metal disilicides (right) [
Fig. 11. (a) Crystal structure of tetragonal transition metal disilicide (left), hexagonal transition metal disilicides (right) [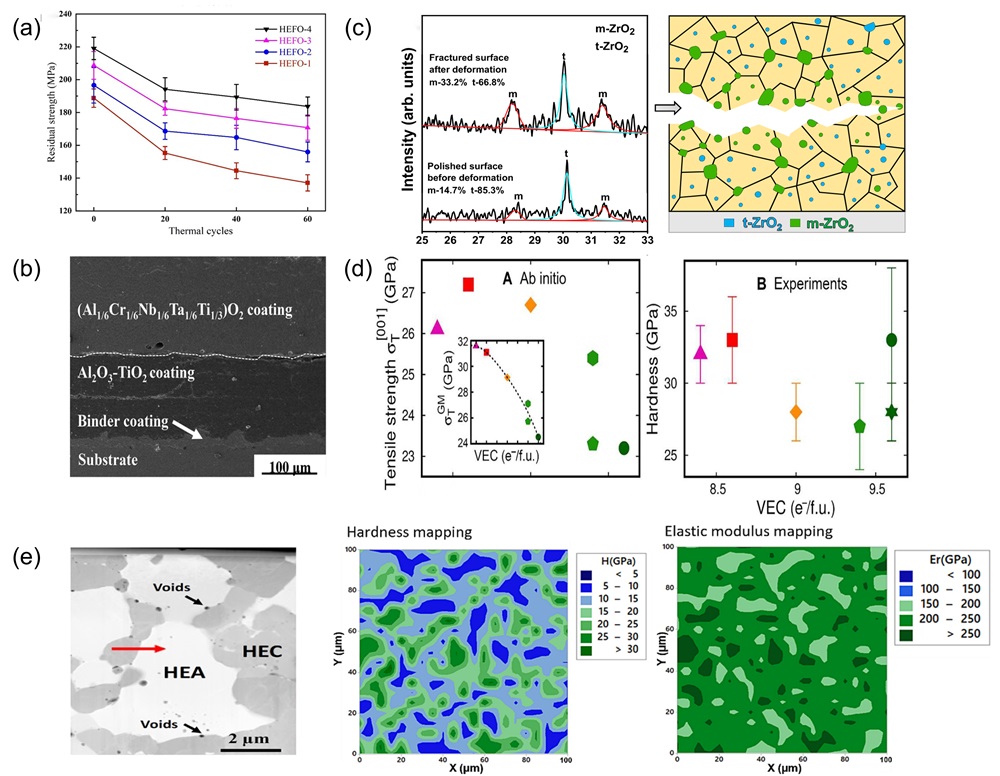 Fig. 12. (a) Residual flexural strength after cyclic thermal shock at 1500℃ [
Fig. 12. (a) Residual flexural strength after cyclic thermal shock at 1500℃ [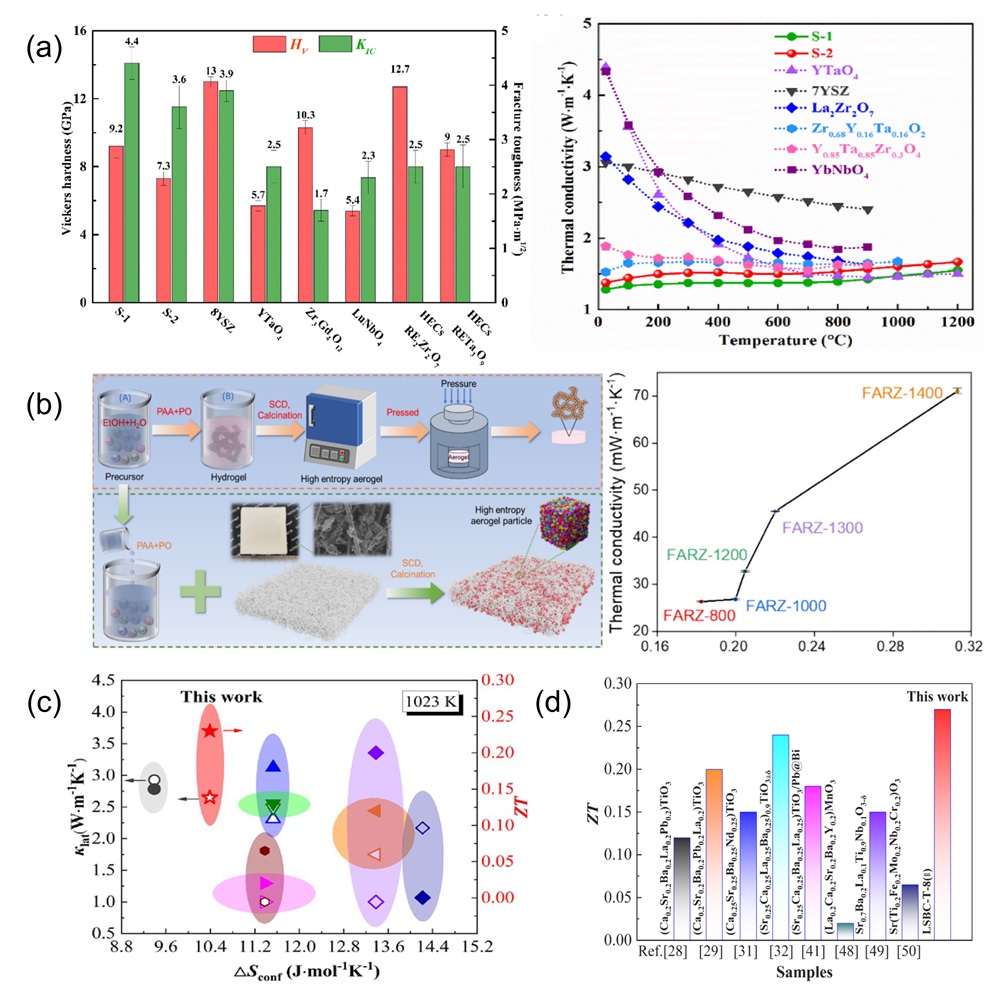 Fig. 13. (a) Mechanical property comparisons between dual-phase zirconate/tantalate HECs, 8YSZ, YTaO4, and others [
Fig. 13. (a) Mechanical property comparisons between dual-phase zirconate/tantalate HECs, 8YSZ, YTaO4, and others [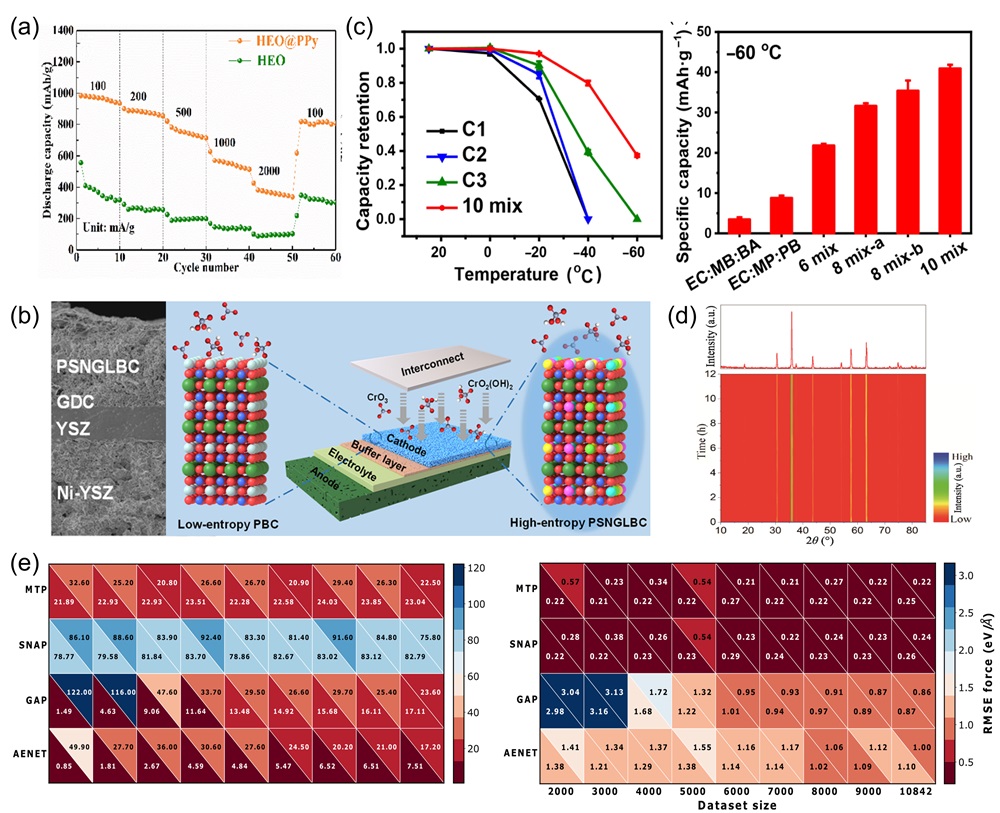 Fig. 14. (a) The rate discharge performance of HEO and HEO@PPy at various current densities; the rate performance of HEO@PPy significantly outperforms that of HEO [
Fig. 14. (a) The rate discharge performance of HEO and HEO@PPy at various current densities; the rate performance of HEO@PPy significantly outperforms that of HEO [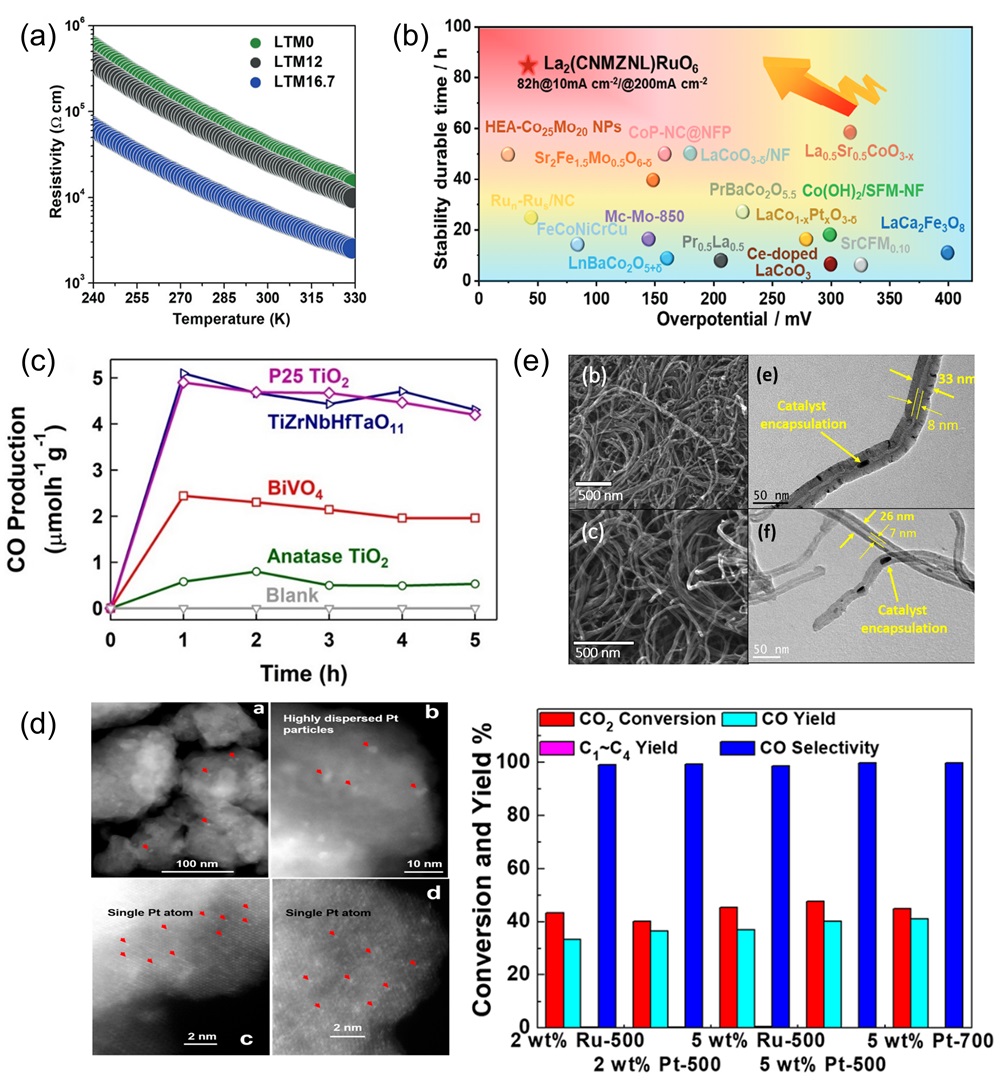 Fig. 15. (a) Temperature-dependent (ρ-T) electrical resistivity test [
Fig. 15. (a) Temperature-dependent (ρ-T) electrical resistivity test [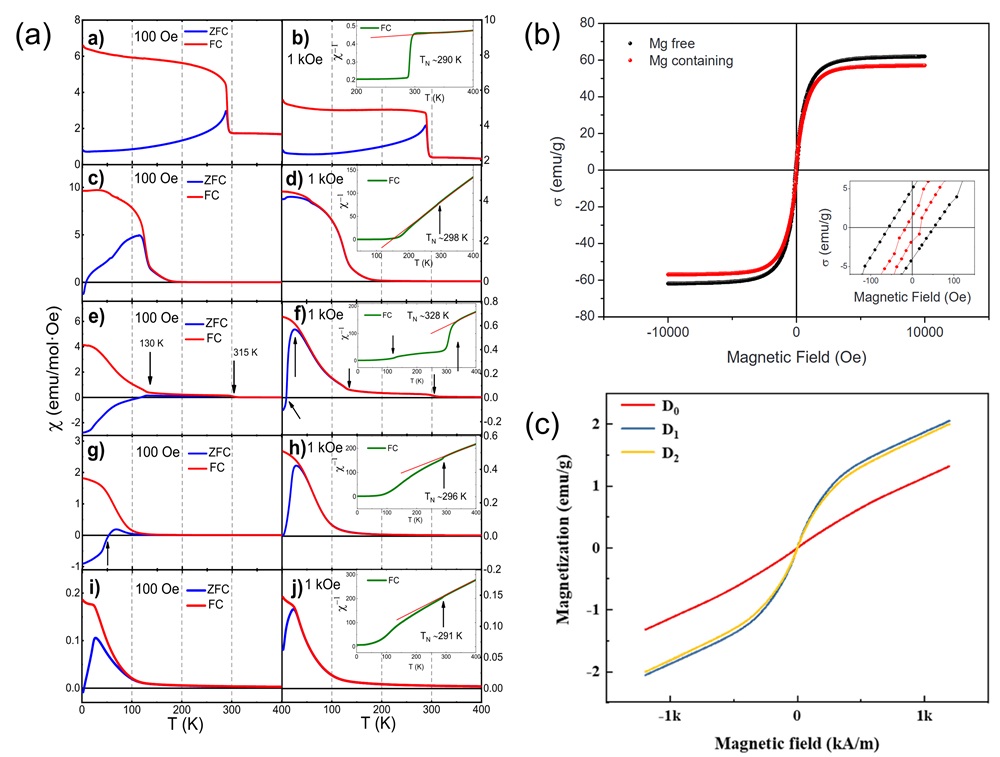 Fig. 16. (a) Magnetic induction strength versus temperature for (a-b) LC, (c-d) LCM, (e-f) LCMF, (g-h) LCMFA, and (i-j) LCMFAG ceramics in ZFC (Zero Field Cooling) and FC (Field Cooling) modes at 100 Oe and 1000 Oe, inset show the χ-1 vs T and the straight line represents the C-W fitting [
Fig. 16. (a) Magnetic induction strength versus temperature for (a-b) LC, (c-d) LCM, (e-f) LCMF, (g-h) LCMFA, and (i-j) LCMFAG ceramics in ZFC (Zero Field Cooling) and FC (Field Cooling) modes at 100 Oe and 1000 Oe, inset show the χ-1 vs T and the straight line represents the C-W fitting [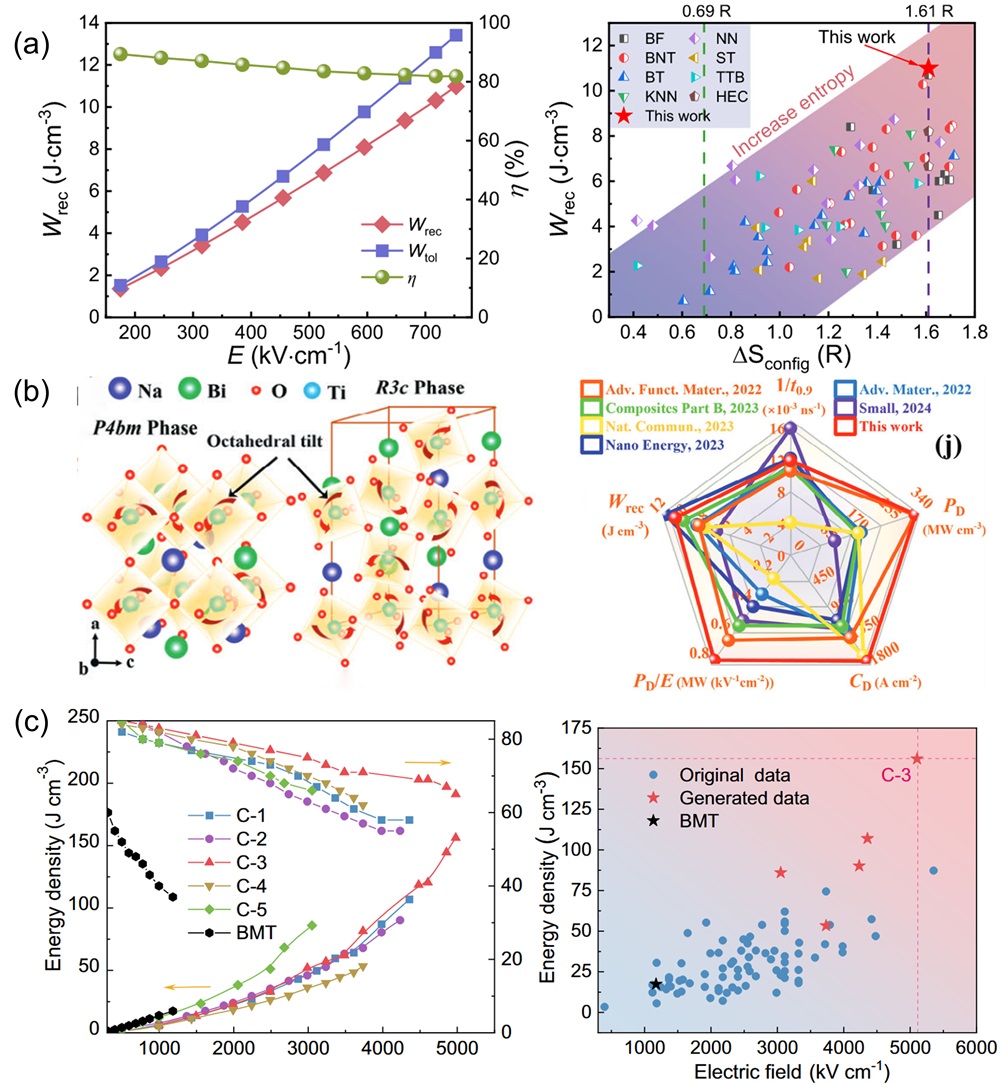 Fig. 17. (a): Wrec and η as a function of electric field and Wrec comparison of (SrBaPbLaNa)Nb2O6 with other entropic materials of different configurations [
Fig. 17. (a): Wrec and η as a function of electric field and Wrec comparison of (SrBaPbLaNa)Nb2O6 with other entropic materials of different configurations [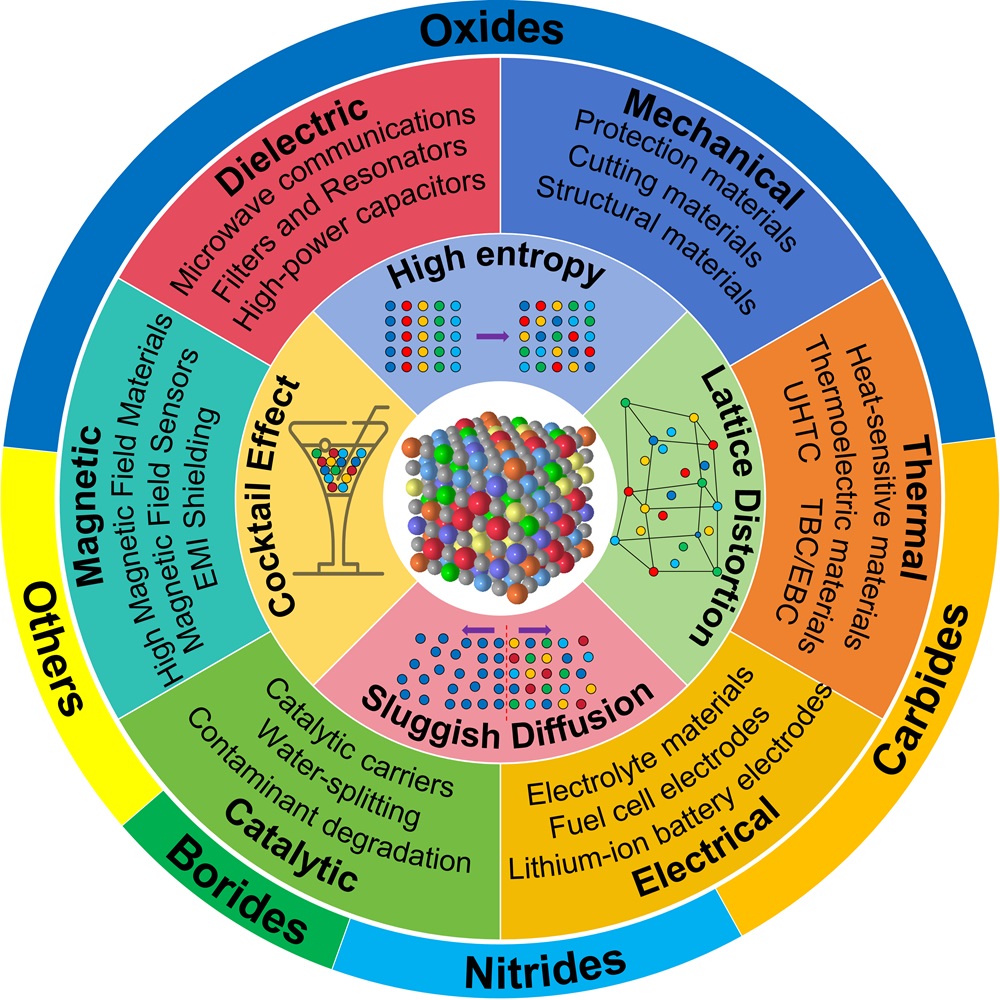 Fig. 18. An overview diagram of HECs. The outer ring shows the percentage of studies on high-entropy oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides and others. The inner rings show the main applications of HECs, as well as the four core effects of high-entropy materials and a schematic of the disordered structure, respectively.
Fig. 18. An overview diagram of HECs. The outer ring shows the percentage of studies on high-entropy oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides and others. The inner rings show the main applications of HECs, as well as the four core effects of high-entropy materials and a schematic of the disordered structure, respectively.